Alumina ceramics have high mechanical strength, large insulation resistance, high hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance and a series of excellent properties, which are widely used in ceramics, textile, petroleum, chemical, construction electronics, and other industries, is the most widely used oxide ceramics, the largest production, and sales of ceramic new materials.
High-aluminum porcelain is a ceramic with Al2O3 and SiO2 as the main components, of which the content of Al2O3 is more than 45%, with the increase of Al2O3 content, the performance indicators of high-aluminum porcelain have been improved. According to the different Al2O3 content, it is also known as 75 porcelain, 80 porcelain, 85 porcelain, 90 porcelain, 92 porcelain, 95 porcelain, 99 porcelain, and so on. High-aluminum porcelain is widely used, in addition to the use of electric vacuum devices and device porcelain, but also a large number of thick film, film circuit boards, spark plug porcelain bodies, textile porcelain, whisker and fiber, abrasives, abrasives and ceramic knives, high-temperature structural materials.
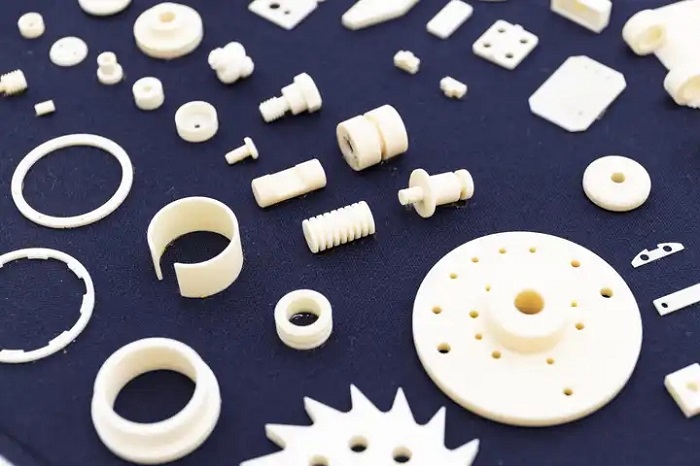

Ceramic injection molding process
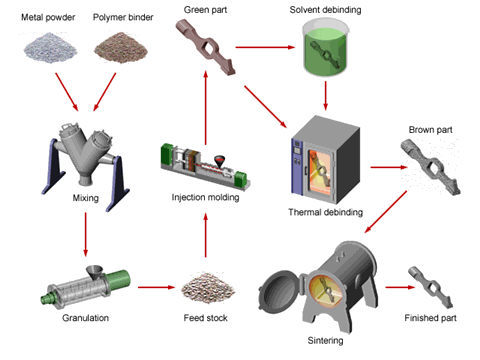
The manufacturing process of precision injection molding of ceramic parts is mainly divided into four links:
① Injection feeding preparation.
The suitable organic carrier (organic matter with different properties and functions) and ceramic powder are mixed, dried, and granulated at a certain temperature to obtain the feed for injection. The role of the machine carrier is to provide the fluidity and strength of the molded body required for ceramic injection molding. At this stage, the interface between the polymer binder the additive, and the ceramic powder is very important. The powder should be uniformly dispersed in the organic carrier without agglomeration and have good rheological properties.
② Injection molding. Injection after mixing
The feed is injected into the mold, and then it is heated into a viscous melt, which is injected into a cold mold at a certain temperature and pressure at a high speed. The melt solidifies into a billet of the desired shape, and then the mold is released. In this stage, the mold design and the flow state of injection melt directly affect the quality of the forming body.
③ Degreasing.
By heating or other physical and chemical methods, the organic matter in the injection molding body is removed. This stage takes a long time, and the forming body is prone to defects. Therefore, it is very important to study the method, mechanism, and kinetics of degreasing.
④ Sintering.
After degreasing, the ceramic body is densified and sintered at high temperatures to obtain compact ceramic parts with the required appearance shape, dimensional accuracy, and microstructure.
Ceramic injection molding parts application field
With the development of science and technology and the improvement of manufacturing technology, alumina ceramics have been more and more widely used in modern industry and modern science and technology.
1) Mechanical aspects. There are wear-resistant alumina ceramic lining bricks, lining plates, lining pieces, alumina ceramic nails, ceramic seals (alumina ceramic ball valve), black alumina ceramic cutting tools, red alumina ceramic plunger, and so on.
2) Electronics and electricity. There are all kinds of alumina ceramic baseplates, substrates, ceramic film, high-pressure sodium lamp transparent alumina ceramics various alumina ceramic electrical insulation porcelain, electronic materials, magnetic materials, and so on.
3) Chemical industry. Alumina ceramic chemical packing ball, alumina ceramic microfiltration membrane, alumina ceramic corrosion resistant coating, and so on.
4) Medical aspects. There are alumina ceramic artificial bones, hydroxyapatite-coated polycrystalline alumina ceramic artificial teeth, artificial joints, and so on.
5) Building sanitary ceramics. The application of alumina ceramic lining brick and microcrystalline wear-resistant alumina spherical stone for ball mills has been very popular, and the application of alumina ceramic roller rods, alumina ceramic protective tubes,s, and various alumina and alumina bonded refractory materials can be seen everywhere.
6) Other aspects. Various composite and modified alumina ceramics such as carbon fiber-reinforced alumina ceramics, zirconia-reinforced alumina ceramics and other toughened alumina ceramics are more and more used in high-tech fields; Alumina ceramic abrasives and advanced polishing paste play an increasingly important role in machinery and jewelry processing industry; In addition, alumina ceramic grinding medium is more and more widely used in the grinding and processing of raw materials in coating, oil paint, cosmetics, food, pharmaceutical and other industries.

Microceramic injection molding
Microinjection molding is a new technology developed recently, which is suitable for MEMS systems with demanding environments and complex structures. The method can be used for a variety of materials (various ceramics, metals), and the cost is low and has high economic benefits. The manufacture of micro ceramic parts by microinjection molding has become
One of the most competitive products in today’s rapidly growing microelectromechanical products market.
Microinjection molding process ll is an improvement on the ordinary injection process, the process is to mix ceramic or metal powder with the adhesive system, and then at a certain pressure into a complex shape of the micro mold, after heating to remove the adhesive, and finally sintering in a specific atmosphere to become
Micro ceramic parts. In particular, in order to ensure the quality of the finished product, the viscosity of the injection feed should be low, and the mold that is easy to release should be selected.
Low-pressure microinjection molding (LPIM) is suitable for manufacturing ceramic or metal parts, and its biggest advantage is to reduce the process temperature (60 ~ 100 ℃) and injection pressure (3-5 MPa). This is because the process uses low-viscosity paraffin wax as a binder. At present, there is already alumina, oxidation
Micro-ceramic components of zirconium, silicon nitride, lead zirconate titanate (PzT), barium titanate, hydroxyapatite, and aluminum nitride are made by low-pressure microinjection molding

Ceramic injection molding parts
Advantages of JH MIM ceramic injection molding
- Can prepare complex shapes, high precision, high-quality ceramic products.
- Flexible process can be applied to different materials and specifications of ceramic products.
- High production efficiency, can achieve large-scale production.
- Environmentally friendly production process to reduce environmental pollution.
- Application areas of this technology include
- Machinery manufacturing: used to manufacture high-precision, high-quality ceramic tools, ceramic bearings, etc.
Automotive manufacturing: For the manufacture of high-performance ceramic components.
Electronic and electrical manufacturing: For the manufacture of high-precision, high-quality electronic components and electrical components.
Aerospace: For the manufacture of high-performance ceramic parts and spacecraft components.






