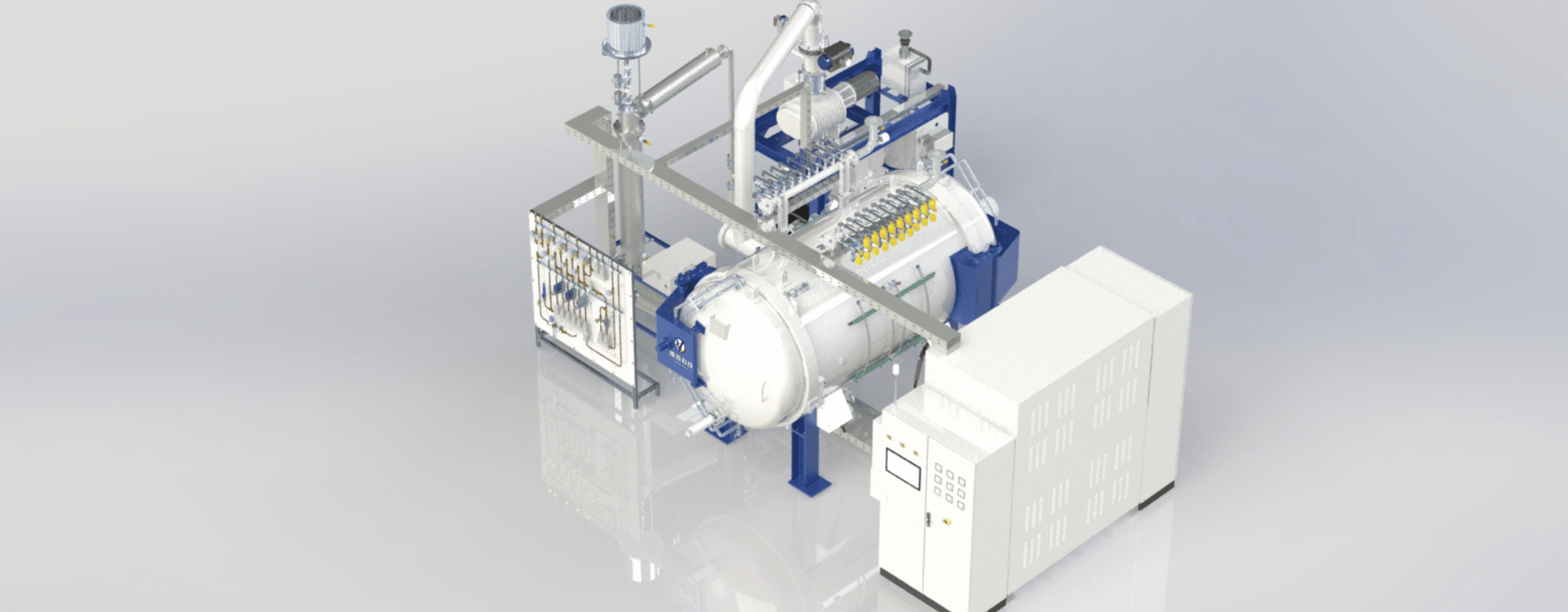
Vacuum degreasing sintering furnace
Vacuum degreasing sintering furnace is mainly used for degreasing and sintering of tungsten alloy, steel bonded gold and other products. It can realize positive and negative pressure degreasing, atmosphere sintering, vacuum sintering and other processes. It can operate in vacuum, Ar/H2 /CH4 gas environment, at temperatures up to 1600℃. The furnace shell adopts double-layer water cooling design, which is suitable for the degreasing treatment of paraffin, rubber and PEG binder, and the dewaxing collection rate (paraffin) is as high as 98%, ensuring the full recovery of paraffin, and greatly reducing the pollution of vacuum pump oil, effectively extending the maintenance cycle of vacuum pump.
| Loading space(W*H*L) | 300*300*1200、400*400*1200、500*500*1500、 500*500*1800、 500*500*2700 |
| Max operating temperature | 1600℃ |
| Vacuum leakage rate | ≤5×10-3 mbarl/s |
| Limiting vacuum | 1Pa |
| Yield of harvest | ≥98%(paraffin) |
| Heating rate (Full load≥1000℃) |
≤7℃/min |
| Temperature uniformity | ≤±5℃ |
| Coercive magnetic bias | ≤±0.25KA/m |
| Cobalt magnetic deviation | ≤±0.15% |
| Temperature measurement method | WRe5-26 two-core thermocouple |
| Have function | Positive dewaxing, negative dewaxing, TORVAC, vacuum sintering,
Static sintering, atmosphere sintering charged cooling, rapid cooling, vacuum cooling |
| Type of process gas | H2 Ar CH4 |

Vacuum Sintering Furnace: A Comprehensive Guide
Vacuum sintering furnace is a crucial piece of equipment in materials science and engineering, widely used for the processing of high-performance materials. It offers a controlled environment for the processing of materials that require vacuum conditions for their synthesis, densification, and melting. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the vacuum sintering furnace, including its definition, purpose, operation, advantages, applications, maintenance, common issues, and future prospects.
-
1. Definition and use
Vacuum sintering furnace is a device that uses high temperatures and vacuum conditions to sinter materials. Sintering is a process where powders are heated to a temperature below their melting point in a controlled atmosphere to bond the particles together. The vacuum sintering furnace is used in various industries, including electronics, ceramics, refractories, jewelry, and others, to produce dense and high-performance materials.
-
2. Working principle
The vacuum sintering furnace works on the principle of heating the material to a temperature suitable for sintering in a vacuum environment. The furnace usually consists of a chamber that can be pumped down to create a vacuum. The material to be sintered is placed inside the chamber and heated using various heating elements. The heat is distributed evenly throughout the material, promoting uniform sintering. The vacuum environment ensures that there is no oxidation or other atmospheric contaminants that can affect the properties of the material.
-
3. Advantages and characteristics
The vacuum sintering furnace offers several advantages over conventional sintering methods. Some of the key benefits include:
Controlled atmosphere: The vacuum environment provides precise control over the atmosphere during sintering, preventing oxidation or absorption of atmospheric gases by the material.
High purity: The absence of atmospheric impurities allows for the production of high-purity materials with consistent properties.
Low residual stress: The vacuum sintering process results in low residual stress in the material, reducing the risk of cracking or warping.
Dense materials: The vacuum sintering process produces dense materials with little or no porosity, enhancing their mechanical properties.
Flexible heating profiles: The ability to control the heating rate and temperature profile allows for precise control over the sintering process.
-
4. Application field
The vacuum sintering furnace has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the main areas of application include:
Electronics: Vacuum sintering is used to produce dense and high-performance ceramics for electronic components such as capacitors, semiconductors, and piezoelectric devices.
Ceramics: Vacuum sintering is employed in the production of high-performance ceramics for various applications, including structural ceramics, ceramic matrices for composites, and dental ceramics.
Refractories: Vacuum sintering is used to produce high-temperature refractories for use in steel and glass industries.
Jewelry: Vacuum sintering is utilized in the production of dense and aesthetically appealing jewelry items such as rings, earrings, and pendants.
Other industries: The vacuum sintering furnace has also found applications in areas such as nanotechnology, spacecraft components, and energy storage devices.
-
5. Operation and maintenance
Operating and maintaining a vacuum sintering furnace requires special attention to ensure safe and effective operation. Some key considerations for operation and maintenance include:
* Operating procedures: Ensure that the furnace is operated according to the manufacturer’s recommended procedures and guidelines. Follow the specified temperature and vacuum conditions closely.
* Material handling: Handle the materials carefully before and after sintering to avoid damage or contamination. Store the materials in a clean and dry environment.
* Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure the proper functioning of the furnace. This includes cleaning the furnace chamber, inspecting heating elements, and replacing worn parts as necessary.
* Safety measures: Implement safety measures such as wearing protective clothing, using gloves when handling hot materials, and ensuring that the furnace is turned off and cooled down before any maintenance work is carried out.
* Training: Ensure that personnel operating the vacuum sintering furnace are properly trained and knowledgeable about its operation, safety procedures, and best practices.
-
6. Common problems and solutions
Like any other piece of equipment, operating a vacuum sintering furnace may encounter some common issues that require attention. Some common problems that may arise include:
* Leaking vacuum: If the vacuum seal is damaged or not properly maintained, it can lead to leaks in the furnace chamber. Regular inspection and replacement of worn seals can prevent this issue.
* Heating problems: Problems with heating elements or improper temperature control can lead to uneven heating or furnace malfunction. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the heating system is essential.
* Material sticking: During the sintering process, materials may stick to the furnace chamber, causing damage. Using appropriate jigs or supports can help prevent this issue.
* Duct blockage: If the vacuum system ducts are not regularly cleaned, they can become blocked, affecting the furnace’s performance. Regular cleaning of the ducts is essential.
-
7. Development trend and prospect
The vacuum sintering furnace technology is continuously evolving, with new advancements and improvements being made to enhance its performance and capabilities. Some of the key trends and developments in this area include:
* Improved vacuum systems: Research and development are ongoing to improve the vacuum systems used in sintering furnaces, aiming to achieve higher vacuums and better control over the sintering process.
* Innovative heating technologies: Developments in heating elements and temperature control systems are enabling more precise and efficient heating during the sintering process.
* Enhanced material properties: Through advanced processing techniques and materials selection, it is possible to achieve better material properties, such as increased density, strength, and corrosion resistance.
* Automation and robotics: The integration of automation and robotics in vacuum sintering furnaces is enabling more efficient, consistent, and reproducible production processes.
* Environmental sustainability: There is increasing focus on sustainable practices in the manufacturing industry, leading to the development of more environmentally friendly vacuum sintering processes and materials.
In conclusion, the vacuum sintering furnace is a crucial tool in a range of industries, from jewelry to advanced materials research. Its ability to produce dense and uniform materials under controlled conditions makes it an essential part of numerous manufacturing processes. With ongoing technological advancements and growing demand for high-performance materials, the future looks bright for the vacuum sintering furnace industry.