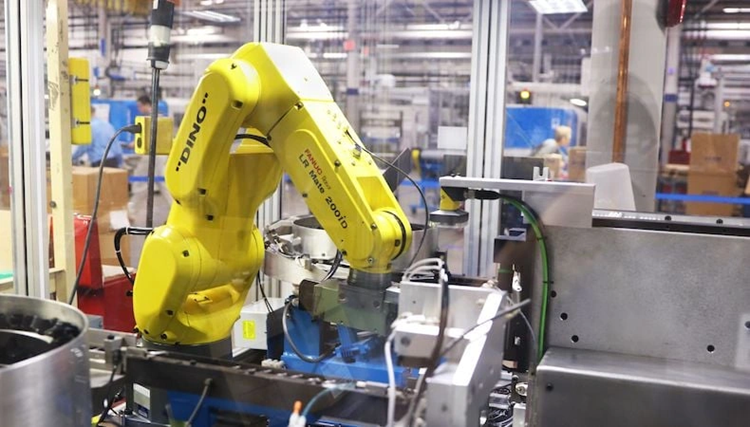

Metal injection molding robotics industrial automation applications just need exceptional precision and complexity that traditional manufacturing methods can’t deliver. MIM produces parts with 96-99% solid density, especially when you have vacuum conditions. These components show excellent mechanical properties like strength and hardness. The manufacturing process creates complex geometries and shapes that work perfectly for uniquely shaped components. It also lets manufacturers mold tiny, intricate parts with tight tolerances.
Modern robotics systems use injection molding automation to streamline production lines. This has substantially boosted efficiency while cutting labor costs. Robots are now used to handle parts, control quality, and execute complex assembly processes. MIM works with a variety of materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and cobalt-chromium alloys. The process offers major cost advantages in high-volume production compared to traditional methods. Process cycles typically run between 2 seconds and 2 minutes, making MIM crucial to meet modern industrial automation’s requirements. JH MIM’s nearly 20 years of experience in Metal injection molding and Powder metallurgy helps deliver precision-engineered products to customers worldwide.
Metal Injection Molding in Robotics: A Precision Manufacturing Backbone
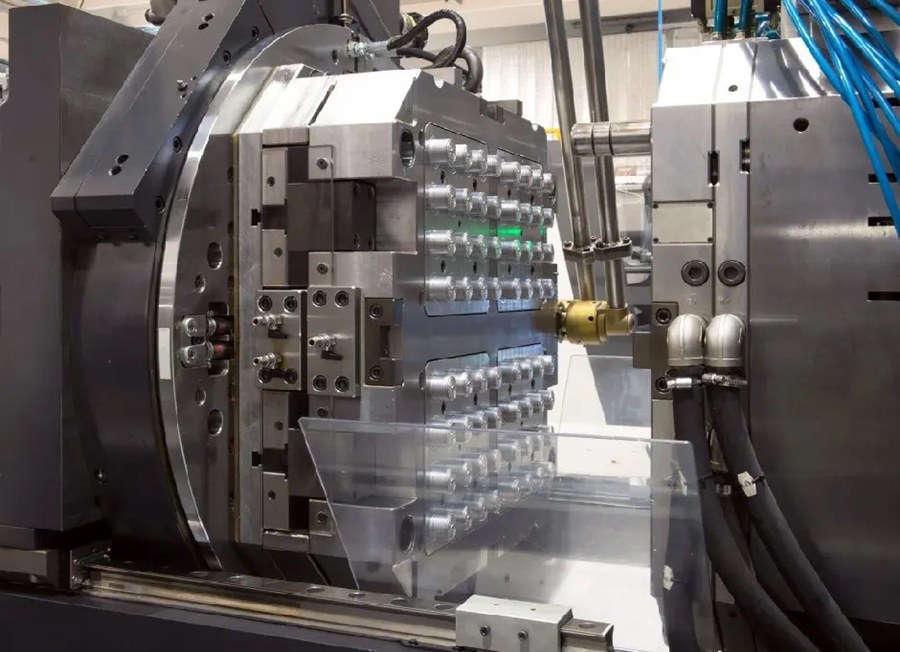

Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines powder metallurgy with plastic injection molding technology to create one of the most versatile manufacturing processes in advanced robotics production. This technology has become the lifeblood of industries that need precision components. Traditional manufacturing methods just can’t match its capabilities.
How MIM Combines Powder Metallurgy and Injection Molding
MIM brings together the strength of traditional powder metallurgy and the design flexibility of plastic injection molding. The process starts when manufacturers create feedstock—a precise mix of fine metal powders and binding agents. They process this feedstock into granular pellets to keep consistency during injection.
The manufacturing happens in four key stages:
- Injection Molding – Manufacturers inject the feedstock into a preheated mold under controlled conditions. This creates a “green” part with 90% metal powder and 10% binder
- Debinding – A catalytic process removes the binder material and turns it into gas. This leaves behind a porous “brown” part
- Sintering – The brown part heats up in a controlled atmosphere. Metal particles fuse and reach 95-99% theoretical density
- Post-Processing – Optional heat treatments or surface finishing boost specific properties based on what the application needs
This step-by-step process lets manufacturers create components with complex internal structures, thin walls (as low as 1mm), and intricate shapes. Traditional methods would struggle or fail to produce these features.
Why Robotics Systems Need High-Tolerance Components
Today’s robotics systems work within incredibly tight operational limits. Each joint, gear, and structural element must sync perfectly to achieve precise movements in automation.
MIM shines here by delivering exceptional accuracy—reaching tolerances of ±0.5%, with some features hitting ±0.3%. These tolerances make all the difference for robotic components like joints and connectors, where precision directly affects performance. MIM parts can achieve a surface finish of Ra0.8-Ra1.2, making them perfect for sensor-embedded components and precision interfaces.
MIM’s material flexibility adds to its value in robotics. The process works with many metals, including:
- Stainless steel
- Titanium alloys
- Cobalt-chromium compositions
- Hard metals and various low-alloy steels
This wide range of materials lets robotics engineers pick the best compositions for their needs—whether they want strength, magnetic properties, or corrosion resistance.
MIM brings big economic benefits to robotics manufacturers. Everything gets used, unlike traditional machining methods that waste material. The process needs less human intervention because it’s largely automated. These advantages make MIM valuable for high-volume production of complex robotics components where consistency matters most.
Robotic systems and MIM workflows have created a positive feedback loop in advanced manufacturing. Robots now help run MIM production lines, which optimize everything from handling to quality control and assembly. The same robotic technologies that benefit from MIM parts now help make those parts better.
JH MIM’s 20 years of experience in metal injection molding and powder metallurgy help them create the precision-engineered products that global robotics manufacturers need for their next-generation automation systems.
Integrating Injection Molding Robots into MIM Workflows
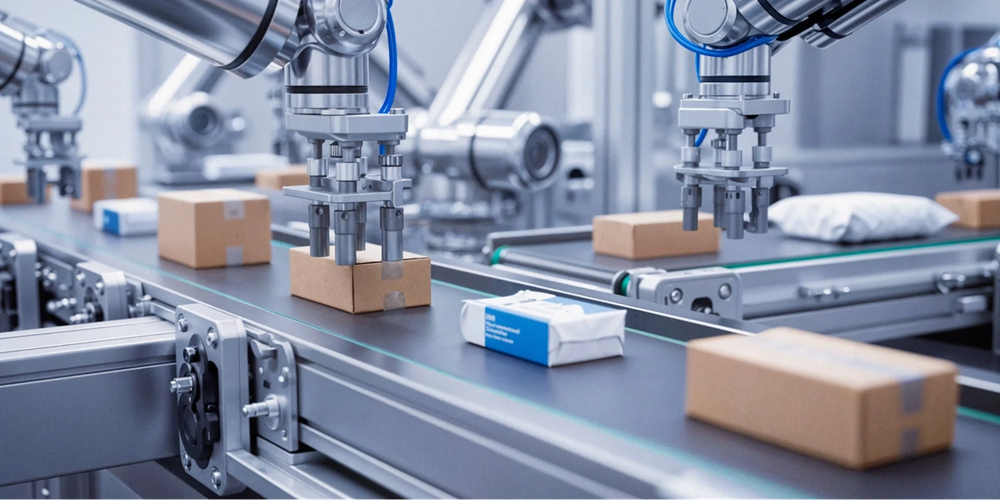

Modern manufacturing facilities are adding robotics faster to metal injection molding operations. This creates production systems that boost both quality and efficiency. The integration of specialized robotic systems throughout the MIM process chain has become crucial for manufacturers who just need to stay competitive in high-precision industries.
Injection Molding Robot Roles in Part Handling and Assembly
Robotic arms have become key components in advanced MIM cells. They execute part handling tasks with exceptional precision and consistency. These six-axis robots arrange themselves to remove freshly molded components and deposit them onto conveyors or load them directly into secondary inspection stations. The robots know how to repeat similar movements within fractions of a millimeter. This prevents damage to delicate or geometrically complex parts—crucial for high-value MIM components.
Custom-designed end-of-arm tooling helps robots handle multiple parts at once or work with specialized inserts. These automated cells often run non-stop for long periods, so they minimize production downtime while delivering consistent quality. Smaller operations or tasks that need human input use collaborative robots (cobots). These cobots work with operators to handle intricate parts that might be tough for larger automation systems.
Plastic Molding Automation for Insert and Overmolding Tasks
Insert molding stands out as one of the most technically challenging aspects of advanced MIM production. The process needs precise placement of components—including threads, pins, or flanges—into the mold before injection. Robotics shines here because insert molding usually involves small parts that human operators struggle to handle consistently.
Overmolding combines separate molded components into a single part and benefits from robotic precision. Manufacturers using PMT’s advanced automation cells get remarkable results through custom systems with vertical, horizontal, or rotary table presses. These systems often include feeder bowls, continuous strip feeding, robotic pick-and-place operations, and built-in testing capabilities.
Safety benefits are clear—robots safely work with high-powered presses and handle hot components, which reduces workplace injury risks. High-volume production environments benefit from automation that delivers quality levels human operators cannot match.
In-mold Labeling and Decoration with Robotic Precision
In-mold labeling (IML) and decorating (IMD) technologies have changed component identification and esthetics through robotic integration. Advanced automation systems employ top-entry, side-entry, or articulated six-axis robots to place labels or decorations accurately. Robots start by placing a preprinted film or label inside the mold cavity, keeping it perfectly aligned during injection.
This approach works better than traditional decoration methods like hot stamping or pad printing. IML/IMD components can feature five-color process in a single shot, barcoding capabilities, UV resistance, and improved durability. The decoration bonds physically with the part instead of being applied on top, creating a permanent bond that resists environmental stressors.
JH MIM brings nearly 20 years of experience in metal injection molding to the table. They’ve built automated workflows that maintain consistent quality in high-volume production runs. Their robotics expertise covers the entire MIM process chain, from the original molding through secondary operations.
We added robotic automation to MIM workflows and saw three main benefits: shorter cycle times, lower labor costs, and better quality consistency. These factors matter most when supplying precision components to the demanding robotics industry.
Designing for Robotics: MIM Capabilities in Complex Geometries
Metal injection molding’s complex geometry capabilities make it the lifeblood technology for precision robotics components. Unlike conventional manufacturing methods, MIM creates intricate parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy that robotic systems need for reliable performance in demanding environments.
Tight Tolerances: ±0.3% Dimensional Accuracy in MIM
MIM achieves remarkable dimensional precision with tolerances of ±0.3% for targeted dimensions. Standard tolerances range from ±0.3% to ±0.5% of the component size. JH MIM’s experience of nearly 20 years helps produce parts with tighter specifications. Some demanding applications can achieve tolerances as precise as ±0.002 inches.
Several vital factors determine tolerance capabilities:
- Tooling precision (baseline for achievable tolerances)
- Shrinkage compensation (critical for tight dimensional control)
- Feedstock composition (affects flow and filling behavior)
- Process parameters control (heat, pressure, injection speed)
- Sintering atmosphere regulation (minimizes distortion)
Advanced mold flow simulation helps optimize gate design for balanced filling and minimizes trapped air that could affect dimensional stability. JH MIM’s closed-loop process monitoring throughout production keeps part-to-part consistency high.
Multi-axis Part Design for Robotic Joints and Actuators
Robotic systems with multiple axes need components that can execute complex trajectories and dynamic movements. MIM excels at producing these intricate geometries, including thin walls, fine features, and internal cavities that robotic joint mechanisms need. This manufacturing versatility lets engineers unite multiple components into single, more efficient parts.
MIM produces components that aid coordinated point-to-point movements along orthogonal X, Y, and Z axes for multi-axis configurations. The process also works with rotational elements (Rx, Ry, and Rz) that can be added to each axis. This achieves up to six-axis configurations with wider capability ranges.
Surface Finish Requirements for Sensor-Embedded Components
Smart machine components with surface-embedded sensors detect deviations from normal operating conditions early. MIM’s ability to achieve surface roughness (Ra) of approximately 1μm creates perfect conditions for sensor integration.
Surface quality affects sensor performance in several ways:
- Optical sensors require consistent surface reflectivity
- Contact-based sensors depend on precise surface dimensions
- Electromagnetic sensors need uniform material properties
MIM delivers components with excellent surface finish straight from sintering that often need minimal secondary processing. This feature is valuable, especially when you have embedded sensors that monitor vibration, temperature, or positioning with exceptional precision.
Cycle Time Optimization and Cost Efficiency in MIM Automation
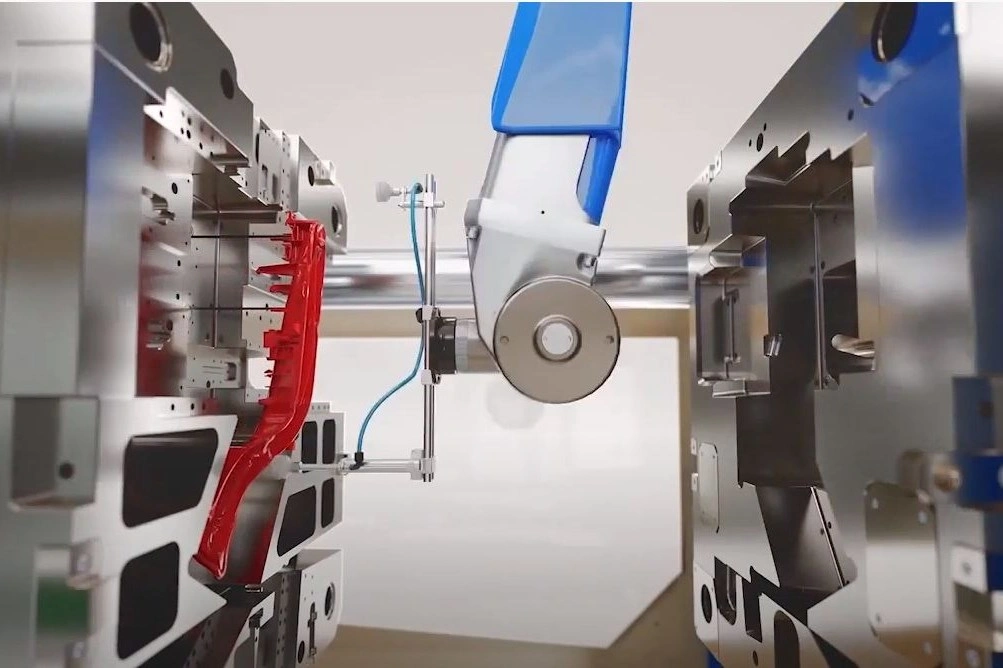
Automation in metal injection molding processes offers two key advantages: optimized cycle times and lower operational costs. Companies need integrated automation systems to stay competitive as manufacturing volumes increase.
Injection Molding Automation for Reduced Downtime
Proper implementation of injection molding automation can cut changeover times by up to 80%. Interactive guidance systems help operators through mold changes step-by-step and minimize machine downtime. Menu-guided approaches significantly reduce errors during mold changes. Automated program steps mean companies don’t need highly skilled personnel.
MIM works best economically when producing large volumes. Companies can quickly recover their original mold creation costs through high-volume production runs. Advanced manufacturing systems connect directly to injection presses. These systems capture critical sensor data in milliseconds and enable real-time process monitoring. Engineers can set parameter limits that trigger alarms or automatically stop production if measurements drift beyond acceptable ranges.
Sprue Picker Robots and Material Recycling Integration
Sprue picker robots let injection molding machines run on their own. They remove and discard sprues so the machine starts its next cycle without human help. Today’s sprue pickers come with solid construction that ensures precise movements with minimal vibration. They also feature rotatable bases for smooth disposal. Take-out times as quick as 0.3 seconds with complete cycle times of 3.0 seconds boost throughput significantly.
Material recycling integration helps cut costs further. MIM creates less waste and scrap while needing smaller material inventories. Robotic sprue pickers connect to conveyor systems that move discarded materials straight to regrinding stations. This creates a closed-loop recycling system that makes the most of available materials.
Labor Cost Reduction through Machine Tending Robots
Industrial manufacturers lose about $50 billion yearly due to unplanned downtime. Machine tending robots turn this downtime into productive runtime by loading, unloading, and operating machines continuously. Key benefits include:
- Higher uptime with no idle time between cycles
- 24/7 productivity enabling “lights-out” manufacturing shifts
- Consistent precision without operator fatigue
- Improved workplace safety by removing operators from hazardous tasks
Machine tending automation lets one operator oversee multiple machines. Robots work non-stop without breaks, vacations, or health insurance requirements, which reduces labor costs. Manufacturers struggling with labor shortages find unmanned machine-tending solutions valuable. These solutions enable round-the-clock production that’s crucial to stay competitive.
JH MIM’s Engineering Expertise in Robotics Applications
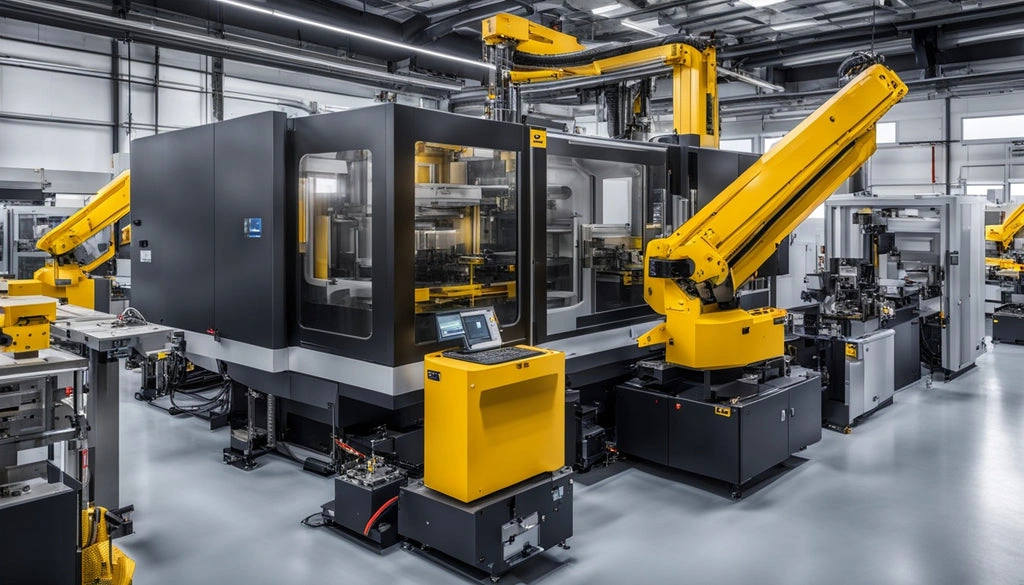

JH MIM stands out in metal component manufacturing for advanced robotic systems. Their engineering team tackles the tough demands of modern automation applications head-on.
20 Years of MIM and Powder Metallurgy Experience
JH MIM’s two decades of work in metal injection molding and powder metallurgy have built deep expertise in creating components that meet strict robotics standards. Their engineering team creates custom metal solutions through controlled atmosphere sintering and advanced debinding techniques. Their work spans industries where precise movement and reliability matter most, from collaborative robots to industrial automation systems.
JH MIM engineered high-precision MIM gears for autonomous navigation systems that needed exceptional accuracy. These components had:
- Complex tooth profiles with ±0.3% dimensional tolerance
- Integrated sensor mounting points
- Specialized surface treatments for reduced friction
- Material compositions optimized for wear resistance
These parts lasted 40% longer than traditional manufacturing methods and made the system lighter overall.
Global Supply Chain Support for Robotics OEMs
JH MIM delivers reliable supply chain solutions to robotics manufacturers worldwide. Their customer support network features dedicated engineering teams for collaborative design optimization and quality checks that go beyond industry standards. They offer flexible manufacturing capacity that adapts to different production needs. This setup helps robotics manufacturers keep consistent quality across their international operations and launch new automation solutions faster.
Conclusion
Metal injection molding has become the life-blood of advanced robotics systems. This 20-year-old technology delivers unique precision and complexity that traditional manufacturing methods can’t match. The combination of powder metallurgy with injection molding techniques creates components with exceptional dimensional accuracy—reaching tolerances as tight as ±0.3%—which modern automation applications just need.
MIM’s benefits go way beyond the reach and influence of precision. These components are ideal for sophisticated robotic joints and actuators due to their complex geometries, multi-axis designs, and sensor-ready surface finishes. The material options include stainless steel, titanium, and specialized alloys. Engineers can meet specific performance requirements while keeping consistency across high-volume production runs.
Automation has reshaped the scene of MIM manufacturing through shorter cycle times, less downtime, and lower labor costs. Robotic systems now handle everything from part removal and inspection to insert placement and secondary operations. This creates a cycle where robotics both benefits from and improves MIM production.
The economic advantages make MIM the preferred manufacturing method for robotics components. The process wastes less material compared to traditional machining and delivers cost benefits for high-volume production. Automated sprue removal and material recycling systems use materials efficiently, which improves sustainability and profitability.
JH MIM leads this manufacturing development with nearly two decades of specialized experience in metal injection molding and powder metallurgy. Their expertise includes the entire production chain—from shared design optimization to quality assurance protocols that exceed industry standards. This detailed approach helps robotics manufacturers worldwide maintain component quality consistency across international operations. They can also reduce time-to-market for next-generation automation solutions.
The connection between MIM and robotics will without doubt grow stronger as automation continues to expand across industries. Metal injection molding has proven itself more than a manufacturing method—it’s an enabling technology that makes the precision, complexity, and reliability of modern robotics systems possible.
Key Takeaways
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) has emerged as the precision manufacturing backbone for advanced robotics, delivering exceptional dimensional accuracy and complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve.
• MIM achieves ±0.3% dimensional accuracy – Critical for robotic joints and actuators requiring precise movement and reliable performance in demanding automation applications.
• Robotic automation reduces MIM cycle times by 80% – Automated systems minimize downtime, enable 24/7 production, and significantly cut labor costs through continuous operation.
• Complex geometries consolidate multiple components – MIM creates intricate internal structures and thin walls impossible with traditional manufacturing, reducing assembly complexity.
• Material versatility supports diverse applications – Process accommodates stainless steel, titanium, and specialized alloys with 96-99% solid density for optimal mechanical properties.
• Cost-effective for high-volume production – MIM minimizes material waste while delivering substantial economic advantages compared to conventional machining methods.
The integration of robotics into MIM workflows creates a powerful synergy where the same precision technologies that benefit from MIM components are now enhancing the manufacturing process itself, driving innovation in both industries forward.
FAQs
Q1. What are the key advantages of metal injection molding for robotics components? Metal injection molding offers exceptional dimensional accuracy (up to ±0.3% tolerance), complex geometries, and the ability to create intricate internal structures. It also provides material versatility and cost-effectiveness for high-volume production of precision parts used in advanced robotics systems.
Q2. How does automation impact the metal injection molding process? Automation in metal injection molding significantly reduces cycle times, minimizes downtime, and cuts labor costs. Robotic systems handle tasks like part removal, inspection, and insert placement, enabling 24/7 production and improving overall efficiency and consistency.
Q3. What materials can be used in metal injection molding for robotics applications? Metal injection molding supports a wide range of materials suitable for robotics, including stainless steel, titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium compositions, and various low-alloy steels. This versatility allows engineers to select optimal compositions for specific performance requirements in robotic components.
Q4. How does metal injection molding compare to traditional manufacturing methods for robotics parts? Metal injection molding outperforms traditional methods by producing complex shapes with tighter tolerances, generating less waste, and offering substantial cost benefits for high-volume production. It also allows for the consolidation of multiple components into a single, more efficient part.
Q5. What role does surface finish play in metal injection-molded components for robotics? The surface finish of metal injection molded parts is crucial for robotics applications, especially for sensor-embedded components. MIM can achieve a surface roughness (Ra) of approximately 1μm, creating an ideal foundation for integrating sensors that monitor vibration, temperature, or positioning with exceptional precision.
