Understanding the Pros and Cons of Metal Injection Molding vs Forging


Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and Forging represent two distinct methods for manufacturing metal components, often discussed in the context of Metal Injection Molding vs Forging. MIM combines metal powders with binders to create intricate shapes, while Forging uses compressive forces to shape metals and enhance their strength. Understanding the differences between these methods helps you make informed decisions for your projects. Each method offers unique advantages and limitations in areas like strength, durability, design flexibility, and cost. By comparing these factors in the Metal Injection Molding vs Forging debate, you can determine which process aligns best with your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is ideal for producing intricate designs with high precision, making it suitable for industries like medical devices and electronics.
- Forging offers exceptional strength and durability due to grain alignment, making it the preferred choice for critical applications in aerospace and automotive sectors.
- MIM minimizes material waste and is cost-effective for high-volume production, while forging can lead to higher material waste and labor costs, especially for small runs.
- Consider the design complexity of your project: MIM excels in detailed components, whereas forging is better for simpler, robust designs.
- Initial tooling costs for MIM can be high, but they become manageable with large-scale production; forging may have lower initial costs but can be labor-intensive.
- Evaluate the scalability of each method: MIM is highly efficient for mass production, while scaling up forging operations can be challenging and costly.
- Consult manufacturing specialists to determine the best method for your specific project needs, balancing design requirements, budget, and production scale.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM): Process, Benefits, and Limitations
The MIM Process
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines the precision of plastic injection molding with the strength of metal. This process begins with finely powdered metals mixed with a binder material. The mixture forms a feedstock that is ready for molding.
The key steps in MIM include:
- Mixing: Metal powders and binders are blended to create a uniform feedstock.
- Molding: The feedstock is injected into a mold to form the desired shape.
- Debinding: The binder is removed, leaving behind a fragile “green part.”
- Sintering: The part is heated to a high temperature, fusing the metal particles and achieving its final density.
This process allows you to produce intricate parts with high precision and consistency.
Benefits of MIM
MIM offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for specific applications:
- High precision for complex and intricate designs: MIM excels at creating detailed components that would be challenging with other methods. You can achieve tight tolerances and fine details.
- Minimal material waste and high material utilization: The process uses nearly all the material, reducing waste and saving costs.
- Ideal for high-volume production: MIM is highly efficient for producing large quantities of parts. This makes it suitable for industries requiring mass production.
These benefits highlight why MIM is often chosen when design complexity and efficiency are priorities.
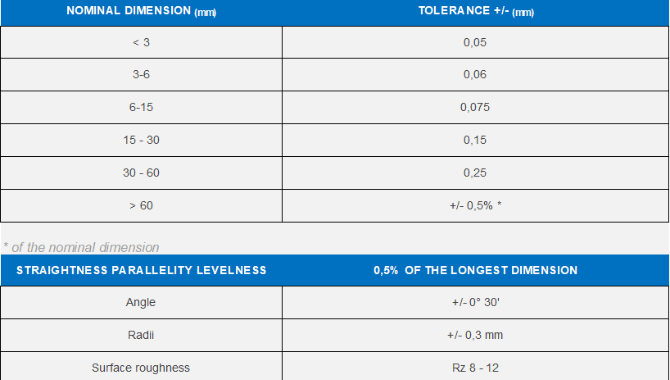
MIM Tolerance
Limitations of MIM
Despite its advantages, MIM has some limitations you should consider:
- Higher initial tooling costs: The molds required for MIM can be expensive, especially for small production runs.
- Limited to smaller-sized components: MIM works best for small and lightweight parts. Larger components may not be feasible.
- May not achieve the same strength as forged parts: While MIM parts are strong, they may not match the strength and durability of forged components. This difference becomes critical in applications where maximum strength is essential.
Understanding these limitations helps you decide whether MIM aligns with your project requirements or if another method, such as forging, might be better suited.
MIM PARTS
Forging: Process, Advantages, and Drawbacks
The Forging Process
Forging shapes metal by applying compressive forces. This process alters the metal’s internal structure, improving its strength and durability. You start with a metal workpiece, which is heated or kept at room temperature depending on the forging type. Then, tools or dies apply pressure to form the desired shape.
There are three main types of forging:
- Open-die forging: This method uses flat dies that do not enclose the metal entirely. You can create large, simple shapes with this technique.
- Closed-die forging: Also called impression-die forging, this method uses dies that completely enclose the metal. It produces more precise and complex shapes.
- Cold forging: This process shapes metal at room temperature. It enhances the surface finish and dimensional accuracy of the part.
Each type of forging serves specific purposes, allowing you to choose the best method for your application.
Advantages of Forging
Forging offers several benefits that make it a reliable choice for many industries:
- Exceptional strength and durability due to grain alignment: The compressive forces align the metal’s grains, which increases its mechanical properties. This makes forged parts stronger and more resistant to wear and fatigue.
- Suitable for larger components and critical applications: Forging handles the production of large, heavy-duty parts. You can rely on it for components used in demanding environments.
- Proven reliability across industries like aerospace and automotive: Forged parts have a long history of success in industries where safety and performance are critical. You often see them in aircraft engines, car suspensions, and heavy machinery.
These advantages highlight why forging remains a trusted manufacturing method for high-strength applications.
Drawbacks of Forging
Despite its strengths, forging has limitations you should consider:
- Limited design flexibility for intricate shapes: Forging struggles to produce highly detailed or complex designs. If your project requires intricate features, this method may not meet your needs.
- Higher material waste compared to MIM: The process often involves trimming excess material, which increases waste. This can lead to higher material costs.
- Labor-intensive for small-scale production: Forging requires significant manual effort, especially for smaller production runs. This can make it less efficient and more expensive for low-volume projects.
Understanding these drawbacks helps you evaluate whether forging aligns with your project goals or if another method, such as MIM, would be more suitable. Comparing Metal Injection Molding vs Forging allows you to weigh these factors effectively.

Metal Forging parts
Comparing Strength and Durability in Metal Injection Molding vs Forging
Strength and Durability of Forged Parts
Forging creates components with unmatched strength and durability. The process aligns the metal’s grain structure, which enhances its mechanical properties. This alignment reduces weak points and improves resistance to wear, fatigue, and impact. You can rely on forged parts for applications where maximum strength is essential.
Industries like aerospace and automotive depend heavily on forged components. In aerospace, forged parts ensure safety and performance in critical areas such as aircraft engines and landing gear. Automotive manufacturers use forging to produce suspension systems and drivetrain components that withstand extreme stress. These examples highlight why forging remains a top choice for high-strength applications.
Strength and Durability of MIM Parts
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) produces parts with good strength, though they may not match the durability of forged components. The sintering process in MIM creates dense and solid parts, but the absence of grain alignment limits their mechanical properties. For applications where moderate strength suffices, MIM offers a practical solution.
You can use MIM parts in scenarios where intricate designs and lightweight components are priorities. Industries like medical devices and electronics benefit from MIM’s ability to create detailed parts without compromising functionality. While MIM may not replace forging in high-stress environments, it provides sufficient strength for many specialized applications.
Design Complexity and Flexibility in Metal Injection Molding vs Forging

MIM for Complex and Intricate Designs
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) stands out when you need parts with intricate details and precise dimensions. The process allows you to create components with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods. MIM molds can replicate fine features, sharp edges, and thin walls with remarkable accuracy. This capability makes it an excellent choice for projects requiring high levels of detail.
Industries that demand precision and complexity benefit significantly from MIM. For example:
- Medical devices: MIM produces surgical instruments, orthodontic brackets, and implantable components with exact specifications.
- Electronics: The method creates small, detailed parts like connectors, sensors, and housings for electronic devices.
- Consumer goods: MIM enables the production of intricate components for watches, eyeglasses, and other high-end products.
By choosing MIM, you gain the ability to manufacture detailed parts efficiently, especially for applications where precision is non-negotiable.
Forging for Simpler and Robust Designs
Forging excels when your project requires strong and durable components with straightforward designs. The process shapes metal through compressive forces, which enhances its mechanical properties. However, forging struggles to achieve the same level of detail as MIM. The tools and dies used in forging are better suited for creating simpler shapes with fewer intricate features.
Challenges arise when you attempt to forge parts with fine details or complex geometries. The high-pressure environment and the nature of the process make it difficult to produce sharp edges or thin sections. This limitation often leads to additional machining or finishing steps, increasing production time and costs.
Despite these challenges, forging remains a reliable choice for robust designs. Industries like aerospace and automotive rely on forged parts for critical applications, such as engine components and suspension systems. These parts prioritize strength and durability over intricate details, making forging the ideal manufacturing method.
When comparing Metal Injection Molding vs. Forging, consider your project’s design requirements. If you need intricate and precise parts, MIM offers unmatched flexibility. For simpler, heavy-duty designs, forging provides the strength and reliability you need.
Cost Considerations in Metal Injection Molding vs Forging
Production Costs
Initial tooling costs for MIM vs forging
When you evaluate production costs, the initial tooling expenses play a significant role. Metal Injection Molding (MIM) requires specialized molds, which can be expensive to produce. These molds are designed precisely to create intricate shapes, making them a high upfront investment. However, this cost becomes more manageable when you plan for large-scale production, as the tooling expenses spread across a higher number of parts.
Forging, on the other hand, involves simpler tools and dies, especially for open-die forging. The initial costs for forging tools are generally lower than those for MIM molds. Yet, if you opt for closed-die forging, the tooling costs can increase significantly due to the need for custom dies. For small production runs, forging may offer a cost advantage over MIM.
Labor and operational costs for each method
Labor and operational costs differ greatly between these two methods. MIM relies heavily on automated processes, reducing the need for manual labor. This automation ensures consistent quality and lowers labor expenses, especially for high-volume production. Operational costs for MIM also tend to be predictable, as the process minimizes material waste and streamlines production.
Forging, in contrast, often requires skilled labor to operate machinery and handle the metal workpieces. This is particularly true for open-die forging, where manual adjustments are necessary. The labor-intensive nature of forging can increase costs, especially for small-scale production. Additionally, the energy consumption in forging, particularly for heating metal, adds to the operational expenses.
Material Costs
Material efficiency in MIM vs material waste in forging
Material efficiency is a key factor when comparing Metal Injection Molding vs Forging. MIM excels in this area by utilizing nearly all the material during production. The process generates minimal waste, as the feedstock is injected directly into the mold, leaving little excess material. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Forging, however, often results in higher material waste. Excess material, known as flash, is trimmed off during the process, especially in closed-die forging. While this waste can sometimes be recycled, it still adds to the overall material costs. If your project prioritizes material efficiency, MIM offers a clear advantage.
Cost implications of using different metals
The choice of metal significantly impacts costs in both methods. MIM works best with finely powdered metals, which can be more expensive than bulk metal used in forging. However, the high material utilization in MIM offsets this cost to some extent. For projects requiring exotic or high-cost metals, MIM’s efficiency can make it a more economical choice.
Forging uses solid metal workpieces, which are generally less expensive than powdered metals. Yet, the material waste in forging can increase costs, particularly when working with premium metals. If you need to minimize material expenses, consider the type of metal and the efficiency of each method.
Scalability
Suitability of MIM for high-volume production
MIM shines when it comes to scalability. The process is highly efficient for producing large quantities of parts with consistent quality. Once you invest in the molds, the per-unit cost decreases significantly as production volume increases. This makes MIM an ideal choice for industries requiring mass production, such as electronics and medical devices.
Challenges of scaling up forging operations
Scaling up forging operations presents unique challenges. The process often requires additional machinery, skilled labor, and energy resources to meet higher production demands. Forging also struggles to maintain cost efficiency at larger scales, especially for complex designs. If your project involves high-volume production, forging may not offer the same level of scalability as MIM.
Metal Injection Molding and Forging offer distinct advantages, making each suitable for specific applications. MIM excels in producing intricate designs and supports high-volume production with efficiency. Forging, on the other hand, delivers unmatched strength and durability, ideal for critical and heavy-duty components.
To choose the right method, consider your project’s requirements, including design complexity, budget, and production scale. Evaluate the strengths of both processes to align with your goals. For expert advice, consult manufacturing specialists who can guide you toward the best solution for your needs.
