Definition:
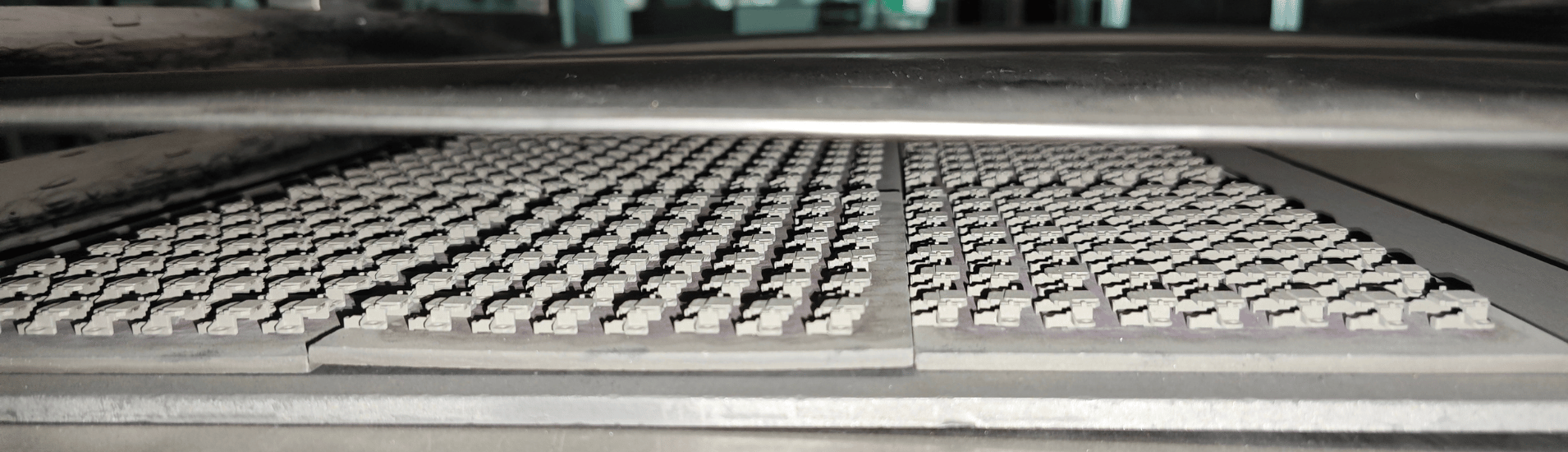
Metal injection molding
It is usually used to make products with small sizes, large quantities, and complex structures. Most MIM parts are made of ferrous metals, such as iron, stainless steel, tungsten alloy, titanium alloy, etc.

Die casting
Die casting is a metal casting process in which molten metal is forced into a mold under high pressure. The production process in which the part is ejected from the mold after it has cooled. Most die-casting parts are made of non-ferrous metals, especially zinc, copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin, and tin-based alloys.
Comparing the die-casting process with the metal injection molding process, through the comparison of the following aspects, I can better understand the differences between the metal injection molding and die casting processes and choose a more suitable method:
MIM Manufacturing Process Vs Die Casting Process
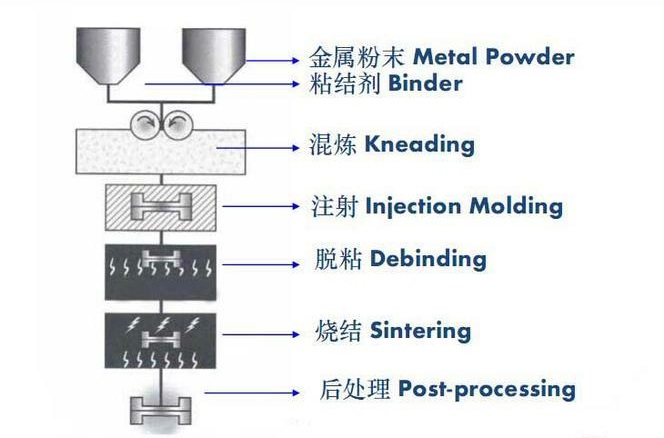
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Process
- Preparing the Feedstock: Combining metal powders with a polymer binder to form a moldable substance.
- Injection Molding: Injecting the feedstock into a mold to form the part.
- Debinding: Removing the binder from the part, which prepares it for sintering.
- Sintering: Heating the part to just below the metal’s melting point to fuse the metal particles.
- Finishing: Additional processes such as machining or heat treatment to meet specific tolerances or properties.
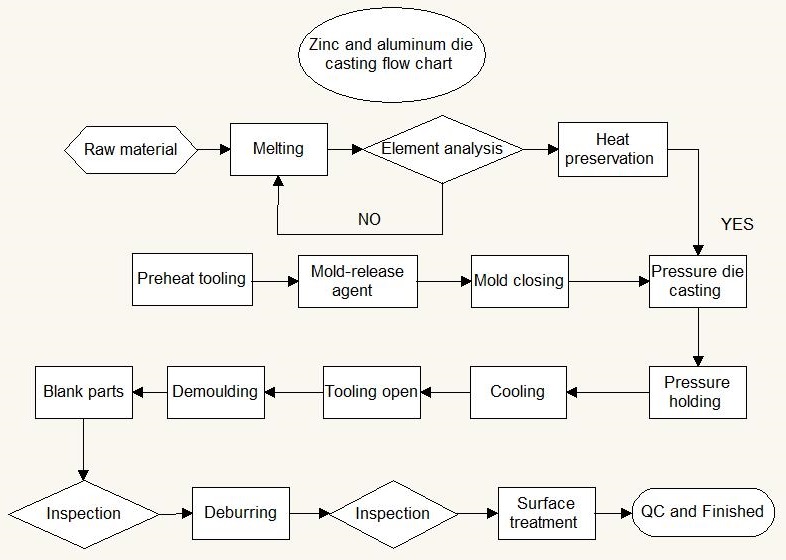
Die Casting Process
- Die Preparation: Applying a lubricant and heating the die for optimal casting conditions.
- Injection: Forcing molten metal into the die under high pressure.
- Cooling: Allowing the metal to solidify within the mold.
- Ejection: Opening the die and removing the cast part.
- Trimming: Removing excess material from the final part.
Selection of materials
Best Material for Metal Injection Molding
- Ferrous Alloys: Steel, stainless steel, iron nickel magnetic alloy, Invar, Kovar, nickel base superalloy.
- Tungsten Alloys: Tungsten heavy alloy, tungsten copper, molybdenum, molybdenum copper.
- Hard Materials: Cermets, cemented carbides.
- Special Materials: Titanium alloy, cobalt chromium.
Materials for Die Casting
- Non-Ferrous Alloys: Lead, pewter, tin-based alloy, magnesium, copper, aluminum, zinc.
Metal Injection vs Die Casting – Key Applications
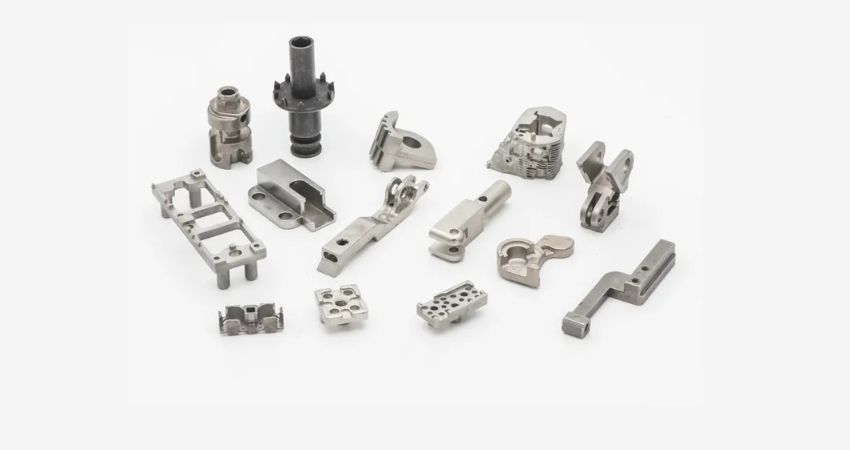
MIM Parts Examples
- Medical: Joint replacements, articulation gears, devices for drugs.
- Automotive: Turbochargers, rocker arms, shift levers.
- Aerospace: Flap screws, valve holders, engine components.
- Electronics: Heat sinks, cold plates, phone components.

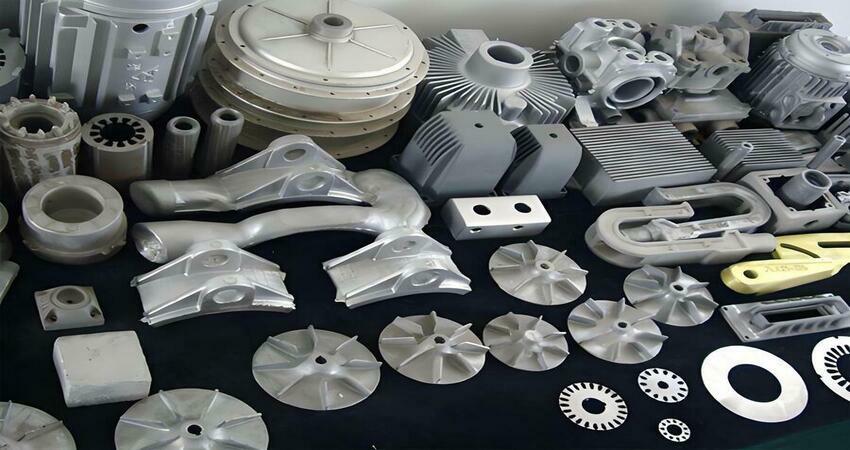
Die Casting Parts Examples
- Automotive: Gear housing, transmission housing, engine components.
- Medical: Hospital equipment controls, surgical devices, blood analysis machines.
- Recreation: RV chassis, marine undercuts, hydrostatic axles.

Product accuracy
The precision of casting is low, and CNC is usually required in the background to ensure the tolerance.
While the precision of MIM process is relatively high. Unless the tolerance is very high, there is generally no need for secondary CNC machining
The surface finish of the product
The casting finish is low, and there are many burrs on the surface. It is necessary to increase the deburring process, and the surface must be ground or sandblasted to maintain the surface finish.
The surface finish of MIM products is very high, usually Ra 0.8-1.6 um;
Product size
The cost advantage of MIM lies in the production of products less than 100g, and casting has more advantages in products larger than 100g;
Molds life
Usually, the mold life of MIM is 200000-300000 times, and the service life of casting mold is about 100000 times.
MIM shows superior efficiency with less than 5% waste generation, compared to die casting which can have higher levels of scrap and waste due to excess material in gates, sprues, and runners.
Pros and Cons of MIM and Die Casting
Metal Injection Molding Pros
- Allows for high dimensional accuracy and complex shapes.
- Suitable for a wide range of materials and surface treatments.
Metal Injection Molding Cons
- Higher costs and lower die life.
- Possible shrinkage of parts up to 30%.
Die Casting Pros
- More cost-effective for large production volumes.
- Suitable for large parts and allows for a high degree of automation.
Die Casting Cons
- Potential for porosity in parts.
- Higher initial setup and mold costs.
Tags Metal Injection Molding | MIM Materials | Design
More Resources:
Die Casting – Source: Wikipedia
Metal Die Casting – Source: Custom Part
Metal Injection Molding – Source: Wikipedia
MIM – Source: Custom Part
