Modern automotive systems rely heavily on precision-engineered crank pulleys. Sintered versions deliver exceptional tolerances of ±0.01mm that ensure smooth and reliable operation. Crankshaft pulleys made through powder metallurgy are a great way to get advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, especially when you have to maintain precise engine system synchronization. These sintered components can handle greater loads and achieve higher strength thanks to their specialized manufacturing process. Automotive manufacturers now prefer these pulleys because their lightweight design helps reduce fuel consumption.
Powder metallurgy’s remarkable material utilization makes it perfect for engine crankshaft pulley systems. These components come with high tooth profile accuracy and need minimal secondary processing. The manufacturing process guarantees core hole tolerances of ±0.015 mm and verticality within 0.025 mm. The main pulley engine integration works better with crankshaft damper pulley technology. This technology separates the belt drive from the crankshaft to minimize vibration and extend component life. The pulleys strike the right balance between structural integrity and weight reduction with density ranges of 6.5-6.8g/cm³. JH MIM brings unique experience of nearly 20 years in Metal Injection Molding and Powder Metallurgy. The company delivers these precision-engineered products globally while meeting high standards verified by TS16949 ISO-9001:2000 quality management system certification.
Powder Metallurgy in Crank Pulley Manufacturing

Powder metallurgy is a key manufacturing process that creates high-performance crank pulleys with great precision and minimal waste. This near-net-shape technique helps produce complex shapes while giving excellent dimensional accuracy.
Material Composition: FC-0205 and FC-0208 Alloys
The strength of sintered crank pulleys comes from their well-engineered material mix. FC-0205 and FC-0208 codes show specific copper levels in iron-based alloys. These materials mix 100 parts iron powder, 3-5 parts copper powder, 1-2 parts graphite powder, and small amounts of chromium. FC-0208 contains about 1.5-3.9% copper and 0.6-0.9% carbon with iron making up the rest. High-temperature sintering gives these alloys excellent mechanical properties, with tensile strength between 240-520 MPa.
Density Control: 6.6–7.0 g/cm³ for Structural Integrity
Getting the right density is vital in making sintered crank pulleys. A density range of 6.6-7.0 g/cm³ will give good structural strength while keeping weight in check. Parts at this density level reach a hardness of 65-90 HRB, which works well for automotive uses. When densities go above 7.0 g/cm³, the benefits move toward better corrosion resistance instead of stronger mechanical properties.
The controlled density affects key mechanical properties like strength, ductility, and hardness. Any changes in the sintering process can create density differences that affect how well the parts work and last.
Steam Treatment and Dacromet Coating for Corrosion Resistance
Untreated sintered parts have tiny pores that make them rust easily, despite their great mechanical properties. Steam treatment creates a thick oxide layer (mostly Fe₃O₄) that bonds strongly to the iron matrix. This is a big deal as it means that hardness, compressive strength, rust resistance, and wear resistance all get better.
The best results come when steam pressure stays at 30±4KPa during treatment. Using two heating stages in steam treatment leads to more weight gain and higher hardness than single-stage heating. This works especially well for parts that need extra work like shaping or vibration deburring.
Adding Dacromet coating gives even more protection. These surface treatments help crank pulleys work well throughout their life, which matters a lot in tough under-hood conditions where moisture and temperature keep changing.
Step-by-Step Sintered Crank Pulley Production
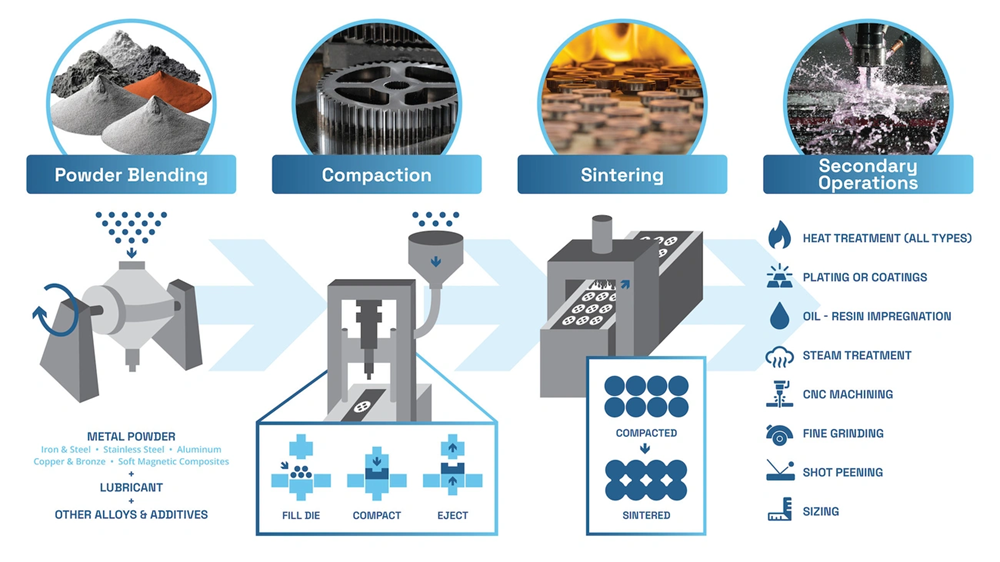
JH MIM uses its 20 years of powder metallurgy experience to manufacture sintered crank pulleys. The process requires precise steps that meet strict automotive standards.
Mixing: Iron, Copper, Graphite, and Chromium Powders
The production starts with precise measurements of raw materials: 100 parts iron powder, 3-5 parts copper powder, 1-2 parts graphite powder, and 0.5-1 part chromium. Specialized equipment blends these materials while spraying water for even distribution. This exact mixture will give a consistent material flow that forms the foundations of strong crankshaft pulleys.
Compacting: 300T Press for Green Part Formation
The powder blend moves to high-capacity compaction presses. Hydraulic pressure turns loose powder into “green” parts that are sturdy enough to handle. The overall density must stay at 6.6g/cm³ or above to ensure proper consolidation. Pressure makes powder particles lock together and creates the simple shape of the engine crankshaft pulley.
Sintering: Hydrogen Atmosphere for Enhanced Strength
Green compacts move through a mesh belt furnace for sintering. This vital process happens in a hydrogen atmosphere, which boosts mechanical properties by a lot. Pure hydrogen gas works best for high-temperature sintering of powder metallurgy parts. It creates stronger bonds between particles without full melting temperatures. The hydrogen environment removes carbon residuals and promotes better metal fusion.
Sizing: Achieving ±0.01 mm Dimensional Accuracy
Pulleys go through sizing operations after sintering to fix dimensional variations. This step ensures crankshaft damper pulleys keep exceptional tolerances of ±0.01mm, which they need for engine component integration. The process needs simpler molds than the original forming process but remains vital for dimensional precision.
Tumbling and Blackening: Surface Finishing Techniques
Surface finishing involves tumbling parts with abrasive media (stone or ceramic) to smooth surfaces and remove burrs. A blackening or steam treatment then creates a protective oxide layer that fights corrosion and makes the surface harder. These features are vital for main pulley engine applications.
Final Inspection and Packaging Standards
Each lightweight crank pulley goes through strict quality checks including size verification, hardness testing, and functional analysis. Anti-rust paper, vacuum sealing, and blister packaging protect the components during shipping. This ensures customers receive perfect products.
Performance Advantages of Sintered Crankshaft Pulleys
Sintered crank pulleys offer multiple performance advantages that boost automotive engine systems. These benefits come from a unique manufacturing process that creates precisely engineered components with exceptional features.
High Load Capacity with HRB70 Hardness
Sintered crankshaft pulleys reach HRB70 hardness or higher, which helps them handle substantial mechanical stress. This hardness level gives excellent wear resistance under high-load conditions. Metallurgical tests show that properly sintered components maintain their structural integrity across many temperatures. The uniform microstructure from powder metallurgy helps deliver consistent performance throughout the part’s life.
Reduced Secondary Machining Requirements
Powder metallurgy technology creates near-net shapes that need minimal secondary operations. Sintered pulleys can achieve dimensional tolerances within ±0.01 mm right after the sintering process. This precision removes many expensive machining steps that cast or forged components need. The high-precision tooth profiles from sintering also guarantee smooth power flow through the drivetrain system.
Lightweight Crank Pulley Design for Fuel Efficiency
Sintered aluminum crankshaft pulleys weigh 50-75% less than traditional cast iron versions. Some automotive applications have shown weight drops from 10.9 lbs (cast iron) to just 3.5 lbs (sintered aluminum). This major weight reduction cuts rotational mass and improves both throttle response and fuel economy by reducing engine load.
Torsional Vibration Damping in Engine Crankshaft Pulley Systems
Engine crankshaft pulleys must control torsional vibrations that happen during operation. These vibrations occur when fluctuating torque on connecting rods makes the crankshaft flex. Poor damping lets these vibrations move through the belt drive system, which can lead to early component failure. Well-designed sintered pulleys with proper elastomer elements turn vibration energy into heat and release it through the pulley housing. This protects accessory belt drive systems and makes engines last longer.
Applications and Compatibility in Automotive Systems
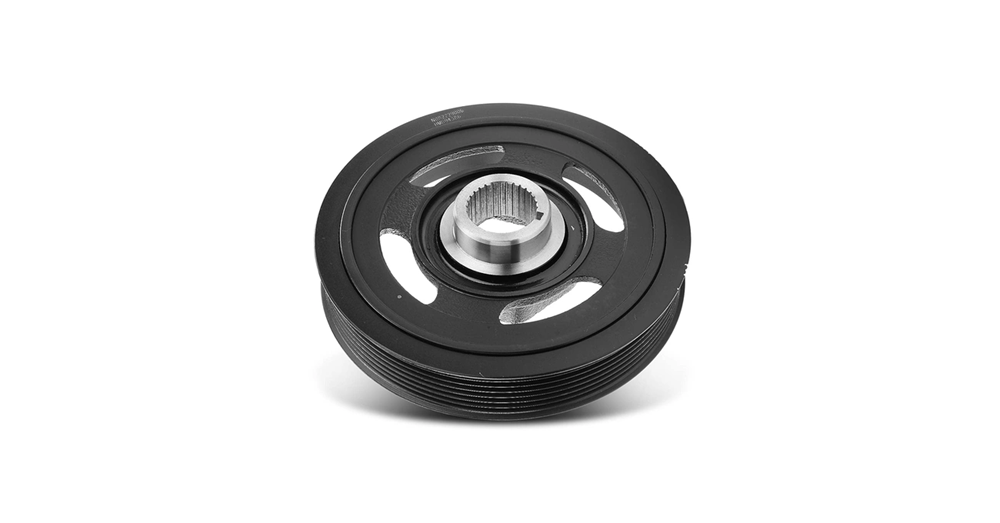

Sintered crankshaft pulleys have become popular in automotive applications of all types due to their precise manufacturing tolerances and superior performance characteristics.
Main Pulley Engine Integration in Timing Systems
Crank pulleys play a vital role in engine timing systems by synchronizing camshaft and crankshaft rotation. The precise timing leads to optimal valve opening and closing sequences that improve engine performance and emissions control. Sintered pulleys with their tight tolerances (±0.01mm) work perfectly in these applications where synchronization drives engine efficiency.
Crankshaft Damper Pulley Use in VVT Engines
Sintered damper pulleys work exceptionally well in Variable Valve Timing (VVT) engines. These components help absorb torsional vibrations that come from the a-cyclical nature of engine combustion. Harmonic balancer pulleys in Chevrolet VVT 2.2L engines prevent timing chain slack and related P0017 codes. The damping effect protects crankshaft bearings from excessive wear and helps the engine run more smoothly.
Compatibility with Audi, Toyota, VW, and Chevrolet Models
JH MIM’s precision-engineered sintered pulleys blend naturally with many vehicle platforms. They work well in Audi A6, A7, and A8 models that use 3.0L V6 engines. Volkswagen applications include different engine configurations where pulleys drive accessories and reduce vibrations. Toyota vehicles benefit from the interchangeability of these pulleys. Chevrolet applications use them to support timing systems in both standard and performance setups.
Conclusion
Sintered crank pulleys are revolutionizing automotive component manufacturing with their precision reaching tolerances of ±0.01mm. This piece explores how powder metallurgy creates components with superior material properties by using carefully controlled compositions of FC-0205 and FC-0208 alloys. These materials deliver the ideal balance of strength and weight when processed at optimal densities between 6.6-7.0 g/cm³.
The manufacturing process shows metallurgical precision at its finest. The process begins by blending iron, copper, graphite, and chromium powders before compaction. The materials then undergo sintering in hydrogen atmospheres to boost strength. Specialized finishing techniques give the components corrosion resistance. This detailed process creates components with remarkable HRB70 hardness that can handle substantial mechanical stress in demanding conditions.
Sintered pulleys stand out from conventional alternatives in performance. Their near-net shape capabilities reduce the need for secondary machining and save production time and resources. The lightweight designs help improve fuel efficiency by cutting down rotational mass. The advanced vibration damping protects the whole drive system from harmful torsional forces.
These precision components prove their versatility in automotive applications across vehicle platforms of all sizes. They play a vital role in timing systems by maintaining critical synchronization between camshaft and crankshaft rotation. Car manufacturers like Audi, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Chevrolet use these pulleys extensively, showing their widespread acceptance in the industry.
JH MIM has spent nearly two decades mastering powder metallurgy and continues to push sintered crank pulley technology forward. Their steadfast dedication to precision engineering helps global customers get components that meet strict standards verified by TS16949 ISO-9001:2000 certification. Without doubt, as automotive systems evolve toward better efficiency and performance, sintered crank pulley technology will remain crucial for manufacturers who want the perfect balance of precision, durability, and weight reduction.
Key Takeaways
Sintered crank pulleys represent a breakthrough in automotive manufacturing, delivering exceptional precision and performance advantages that traditional manufacturing methods cannot match.
• Exceptional Precision: Sintered pulleys achieve ±0.01mm tolerances through powder metallurgy, ensuring perfect synchronization in engine timing systems.
• Superior Material Properties: FC-0205 and FC-0208 alloys with controlled density (6.6-7.0 g/cm³) deliver HRB70 hardness for high load capacity.
• Weight Reduction Benefits: Lightweight design reduces rotational mass by 50-75%, improving fuel efficiency and throttle response significantly.
• Minimal Secondary Processing: Near-net-shape manufacturing eliminates costly machining steps while maintaining precise tooth profiles and dimensional accuracy.
• Enhanced Vibration Control: Built-in torsional vibration damping protects drive systems and extends component lifecycle in VVT engines.
The hydrogen atmosphere sintering process and specialized surface treatments like steam treatment and Dacromet coating ensure these components withstand demanding under-hood environments while maintaining performance integrity throughout their service life across multiple automotive platforms.
FAQs
Q1. How does the design of sintered crank pulleys contribute to engine efficiency? Sintered crank pulleys offer exceptional precision with tolerances of ±0.01mm, ensuring perfect synchronization in engine timing systems. Their lightweight design reduces rotational mass by 50-75%, improving fuel efficiency and throttle response significantly.
Q2. What are the key material properties of sintered crank pulleys? Sintered crank pulleys are typically made from FC-0205 and FC-0208 alloys with a controlled density of 6.6-7.0 g/cm³. This composition allows them to achieve a hardness of HRB70 or greater, providing high load capacity and excellent wear resistance.
Q3. How does the manufacturing process of sintered crank pulleys differ from traditional methods? Sintered crank pulleys are manufactured using powder metallurgy, which involves mixing metal powders, compacting them, and then sintering in a hydrogen atmosphere. This process allows for near-net-shape manufacturing, minimizing the need for secondary machining while maintaining high precision.
Q4. What role do sintered crank pulleys play in vibration control? Sintered crank pulleys, especially when used as damper pulleys, help absorb torsional vibrations caused by engine combustion. This built-in damping effect protects crankshaft bearings from excessive wear and supports smoother engine operation, particularly in Variable Valve Timing (VVT) engines.
Q5. Are sintered crank pulleys compatible with various car models? Yes, sintered crank pulleys are compatible with a wide range of vehicle models. They have been successfully integrated into engines from manufacturers such as Audi, Toyota, Volkswagen, and Chevrolet, demonstrating their versatility and wide acceptance in the automotive industry.
