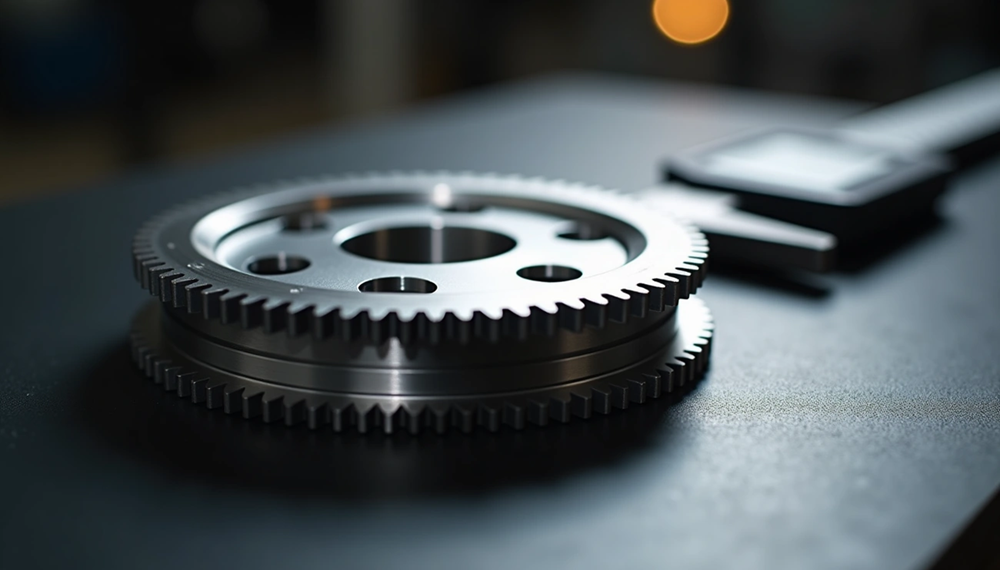

Powder metallurgy manufacturing delivers remarkable precision of ±0.01mm in timing pulleys that ensures critical synchronization in drive systems. These specialized mechanical components have teeth along their outer diameter that engage timing belts. This design prevents slipping and keeps engine parts perfectly arranged. The pulleys made through powder metallurgy technology combine high strength with excellent wear resistance. They maintain stable dimensional precision while working in temperatures from -40°C to +150°C.
The powder metallurgy process has clear advantages over traditional machining methods. Machined timing pulleys waste raw materials and cost more to produce. Metal powder creates sintered timing pulleys without cutting excess material. This leads to cost-effective production and better resource use. The precision-engineered components show impressive results. Their fatigue life is a big deal as it means that they last over 10⁷ cycles at 50% rated load. Quality controls follow ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949:2016 standards to meet tough industrial requirements.
This piece shows how powder metallurgy timing pulleys reach such exceptional precision by dissecting material choices, manufacturing steps, and performance features that make them perfect for critical synchronous drive applications.
Dimensional Precision in Powder Metallurgy Timing Pulleys
Dimensional accuracy is a vital factor that affects how timing pulleys made through powder metallurgy perform. The precision achieved by modern powder metallurgy matches and sometimes exceeds traditional manufacturing methods.
±0.01mm Tolerance Achievement in Sizing Process
The sizing step is vital to achieve precise dimensions in powder metallurgy manufacturing. Manufacturers can reach tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm, which makes these pulleys perfect for high-precision applications. Parts reach about 0.04 to 0.03mm accuracy after sintering, but the sizing operation makes them even more precise. So this process fixes any shape issues from sintering and creates more consistent parts across production runs.
Sizing doesn’t just improve dimensional precision – it gives better surface quality too, which helps the pulleys perform better. The process also cuts down on extra machining work, which saves time and money.
Concentricity Control: ≤0.02mm TIR in Final Inspection
Total Indicator Reading (TIR) measures concentricity, another key dimension for timing pulleys. Standard powder metallurgy timing pulleys can achieve ≤0.02mm TIR. Custom options can reach ≤0.01mm TIR when applications need exceptional precision. These tight controls give phase accuracy even when torque changes.
Manufacturers use coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to check concentricity in final inspection. This detailed quality check keeps the geometric precision needed for synchronous drive applications.
Surface Finish Standards: Ra 0.8μm to 1.6μm
Surface roughness plays a big role in how well timing pulleys work and last. Standard powder metallurgy timing pulleys come with surface finishes between Ra 1.6μm and 3.2μm. Precision components can reach Ra 0.8μm. The most critical parts need specific finishes:
- Tooth flanks get Ra 0.8μm finishes to cut down friction and wear
- Bore and keyway surfaces usually need Ra 1.6μm finishes
These carefully controlled surface finishes create smoother contact surfaces. This reduces friction between parts that touch each other and makes the pulleys more reliable. The surface roughness also helps with corrosion resistance, looks better, and helps coatings stick better when used.
Tight dimensional tolerances, precise concentricity control, and smooth surface finishes make these powder metallurgy timing pulleys perfect for tough jobs that need consistent performance.
Material Selection and Its Role in Dimensional Accuracy
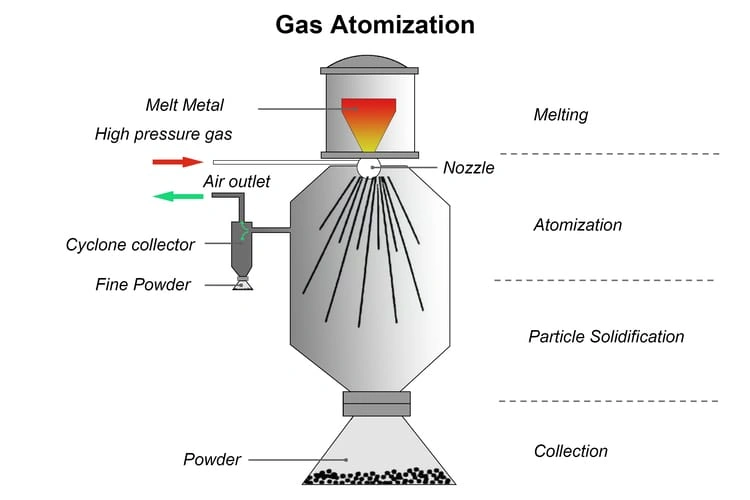
Material properties serve as the foundation for achieving exceptional dimensional accuracy in powder metallurgy timing pulleys. The careful selection of appropriate materials ensures both precision and performance reliability over extended operational periods.
FC-0208 vs FN-0205: Strength and Density Comparison
The two most common materials for precision timing pulleys are FC-0208 and FN-0205, each offering distinct advantages. FC-0208, with a density range of 6.7-6.9 g/cm³, delivers tensile strength between 410-620 MPa and a hardness of 73 HRB. In contrast, FN-0205 features slightly higher density at 6.8-7.0 g/cm³, with tensile strength ranging from 340-830 MPa and hardness of 59 HRB.
FC-0208 consists of iron-copper blends sometimes combined with graphite powder, making it ideal for medium-strength structural applications, including oil pump rotors, shock absorber components, and timing sprockets. FN-0205, containing 2% nickel, provides superior hardenability with improved case depth, thereby enhancing overall durability.
Controlled Porosity for Self-Lubrication and Stability
Porosity represents a critical characteristic in powder metallurgy timing pulleys, serving multiple essential functions. Indeed, controlled porosity allows these components to store lubricants that gradually release during operation. This feature proves especially valuable in applications where continuous external lubrication remains impractical or for components operating under extreme conditions involving high speeds, elevated temperatures, and heavy loads.
The optimization of pore size, concentration, and distribution directly influences both mechanical properties and dimensional stability. According to research findings, substrates with higher relative density (>90%) develop closed pores that limit lubrication capacity, whereas lower density materials with open pores may sacrifice mechanical strength. Therefore, achieving optimal porosity balance remains essential for maintaining precision while ensuring adequate self-lubrication capabilities.
Heat Treatment Impact on Dimensional Stability
Heat treatment significantly enhances the dimensional stability of powder metallurgy components through several mechanisms. Primarily, it relieves internal stress accumulated during manufacturing, homogenizes the microstructure, and minimizes deformation risks. For instance, stress relief annealing reduces tensile stress concentrations that would otherwise cause dimensional changes during machining or long-term use.
Moreover, heat treatment aligns phase composition and grain structure, ensuring consistent thermal expansion across the component. This process effectively eliminates anisotropic grain growth caused by layer-by-layer deposition, reducing directional mechanical imbalance and thermal warping. Consequently, properly heat-treated timing pulleys can maintain dimensional stability within ±0.02mm tolerances even under fluctuating operational temperatures.
Powder Metallurgy Manufacturing Process Steps
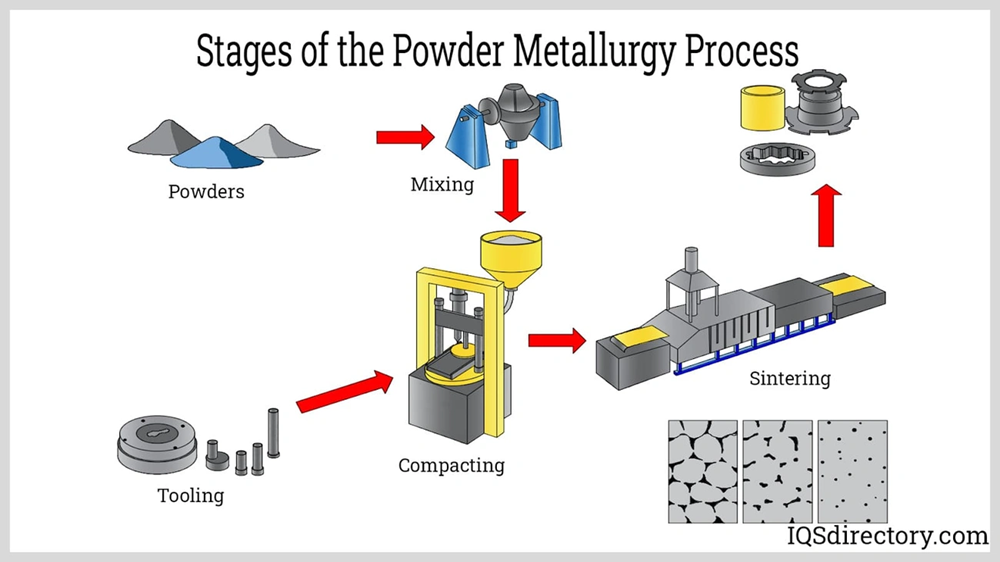
Manufacturing precision timing pulleys through powder metallurgy requires multiple controlled steps that deliver exceptional dimensional accuracy and performance.
Tooling Design for Precision Mold Alignment
Advanced tooling design forms the lifeblood of high-precision powder metallurgy components. Modern tooling materials achieve remarkable tolerances of ±0.002mm with surface finishes as fine as Ra0.2-0.4μm. Components align perfectly with position accuracy within 0.003mm. The Center for Powder Metallurgy Technology (CPMT) provides detailed design guides that help engineers optimize tooling materials for exceptional toughness and wear resistance.
Compacting and Sintering: Maintaining Geometric Integrity
Metal powder transforms into a “green compact” under high pressure inside precisely manufactured dies. These compacts maintain their structural shape effectively. The next step moves these compacts into sintering furnaces at temperatures just below the metal’s melting point. Diffusion and solid-state reactions create strong bonds between particles that result in fully dense and solid components.
Sizing and Calibration for Final Tolerance Correction
Sizing plays a vital role as a secondary operation to improve dimensional precision. Linear tolerances improve to within ±0.01mm while surface finish gets better simultaneously. Sizing dies feature simpler shapes compared to compacting dies, yet they remain essential to the process.
Steam Treatment and Blackening for Surface Hardness
Steam treatment at 500-570°C for 1-2 hours creates a dense magnetite (Fe₃O₄) layer that penetrates the surface and interconnected pores. This process boosts hardness up to 90 HRB, improves corrosion resistance, and enhances wear performance. JH MIM has nearly 20 years of experience in the metal injection molding and powder metallurgy industry, providing precision-engineered products to global customers.
Performance Metrics and Application-Specific Requirements

Powder metallurgy timing pulleys show exceptional performance in many technical applications. Engineers can measure their standardized metrics when they need components that work well under tough conditions.
Fatigue Life: >10⁷ Cycles at 50% Load
Timing pulleys made through powder metallurgy are remarkably durable and keep working beyond 10⁷ cycles at 50% rated load. Testing protocols require measurements at five different stress levels. Each level needs ten repeated measurements to establish reliable statistics. Components that reach stress thresholds without failing have reached their endurance limit under typical test conditions. These parts show predictable performance within ±5.25% of published standards, even with normal variations in fatigue behavior.
High-Speed Operation: Up to 10,000 RPM
These precision pulleys work reliably at speeds up to 10,000 RPM. This makes them perfect for specialized tasks like engraving with small-diameter cutters. The power output drops slightly at these high speeds, but this barely affects typical applications. Such impressive speed capabilities make these parts ideal for advanced drive systems that need both precision and quick motion.
Automotive Use Case: Camshaft and Crankshaft Synchronization
Powder metallurgy timing pulleys play a crucial role in automotive engines by synchronizing crankshaft and camshaft rotation. They help valves open and close with millisecond precision to optimize combustion efficiency. These components work well in both traditional internal combustion engines and hybrid powertrains. You’ll find them in models like Volkswagen EA211 series engines and Toyota TNGA architecture.
Industrial Use Case: CNC and Conveyor Systems
Many industrial machines rely on powder metallurgy timing pulleys. CNC equipment uses these parts to control cutting tool movements with great accuracy. Conveyor systems run at average belt speeds of 65 feet per minute with these pulleys. Some specialized applications might run at speeds up to 100 feet per minute. This is especially true in mining operations where equipment must last under harsh conditions.
JH MIM has spent nearly 20 years making metal injection molding and powder metallurgy products. The company provides precision-engineered products to customers worldwide.
Conclusion
Powder metallurgy timing pulleys showcase exceptional engineering precision. These components achieve remarkable dimensional tolerances of ±0.01mm through meticulous manufacturing control. Material choice plays a crucial role in performance. FC-0208 and FN-0205 each bring unique strength characteristics without compromising precision. The manufacturing process flows through compacting, sintering, sizing, and surface treatments. This creates parts that stay dimensionally stable even when operating conditions change.
These precision components deliver more than just accurate measurements. They handle fatigue resistance beyond 10⁷ cycles at 50% rated load and run reliably at speeds up to 10,000 RPM. This makes them perfect for demanding tasks. The pulleys excel at synchronizing critical engine parts in automotive systems. They also provide exact positioning and movement control in industrial applications.
JH MIM’s track record spans nearly 20 years in metal injection molding and powder metallurgy. The company serves global customers with precision-engineered products. This deep expertise helps modern powder metallurgy timing pulleys maintain ±0.01mm precision while performing optimally in a variety of operating environments.
These components are a big deal as it means that they work better than conventional manufacturing methods. This comes from their controlled porosity for self-lubrication, targeted heat treatments, and specialized surface finishes. Engineers looking for exceptional precision, reliability, and affordable synchronous drive solutions will find powder metallurgy timing pulleys to be the best technical choice. They meet and exceed today’s strict industrial standards.
Key Takeaways
Powder metallurgy timing pulleys achieve exceptional precision through advanced manufacturing techniques and material science, delivering superior performance for critical synchronous drive applications.
• Exceptional Precision: Powder metallurgy achieves ±0.01mm tolerances through sizing processes, with concentricity control ≤0.02mm TIR for critical timing applications.
• Superior Material Properties: FC-0208 and FN-0205 materials provide controlled porosity for self-lubrication while maintaining dimensional stability through optimized heat treatment.
• Proven Durability: These components deliver >10⁷ cycle fatigue life at 50% load and operate reliably at speeds up to 10,000 RPM in demanding environments.
• Cost-Effective Manufacturing: Unlike traditional machining, powder metallurgy eliminates material waste while achieving tighter tolerances through controlled compacting, sintering, and sizing processes.
• Versatile Applications: From automotive camshaft synchronization to CNC precision machinery, these pulleys excel where dimensional accuracy and reliability are paramount.
The combination of advanced metallurgy, precision manufacturing, and rigorous quality control makes powder metallurgy timing pulleys the optimal choice for engineers requiring both exceptional accuracy and long-term performance reliability in synchronous drive systems.
FAQs
Q1. What level of precision can powder metallurgy timing pulleys achieve? Powder metallurgy timing pulleys can achieve remarkable precision of ±0.01mm through advanced manufacturing techniques, particularly during the sizing process. This level of accuracy ensures critical synchronization in drive systems.
Q2. How do powder metallurgy timing pulleys compare to traditional manufacturing methods? Powder metallurgy timing pulleys offer significant advantages over traditional machining methods. They produce less waste, are more economical, and can achieve tighter tolerances. Additionally, they provide excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability across a wide temperature range.
Q3. What materials are commonly used in powder metallurgy timing pulleys? The two most common materials for precision timing pulleys are FC-0208 and FN-0205. FC-0208 is ideal for medium-strength applications, while FN-0205 offers superior hardenability and improved case depth for enhanced durability.
Q4. What is the typical fatigue life of powder metallurgy timing pulleys? Powder metallurgy timing pulleys demonstrate exceptional durability, with a fatigue life exceeding 10⁷ cycles at 50% rated load. This impressive longevity makes them suitable for demanding applications requiring long-term reliability.
Q5. In what industries are powder metallurgy timing pulleys commonly used? Powder metallurgy timing pulleys find applications in various industries. In the automotive sector, they’re crucial for synchronizing camshaft and crankshaft rotation. In industrial settings, they’re used in CNC machinery for precise tool movements and in conveyor systems for managing belt speeds.
