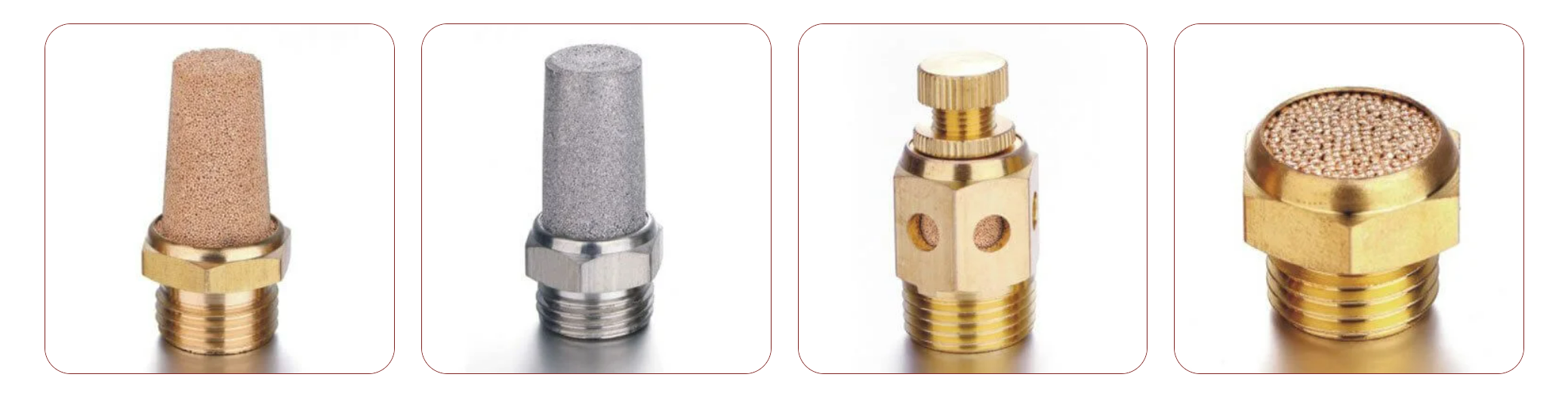

A sintered filter is a specialized filtration device made from powdered materials fused together through heat and pressure. So, what is a sintered filter? Its porous structure allows it to perform critical tasks across various industries.
| Purpose | Description |
|---|---|
| Filtration and Separation | Removes impurities from liquids and gases. |
| Protection of Equipment | Shields sensitive equipment from environmental damage. |
| Flow Control | Regulates liquid or gas flow for stable operations. |
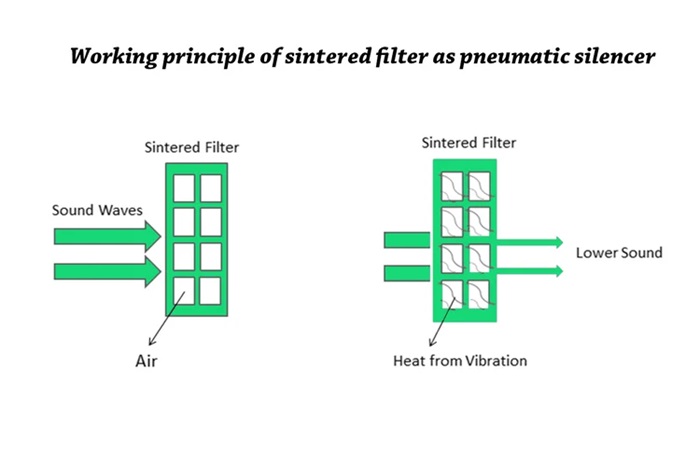
| Noise Reduction | Reduces noise during air exhaust in industrial settings. |
| Chemical Processing | Purifies chemicals by eliminating contaminants. |
| Petroleum Refining | Filters solids and impurities from crude oil. |
| Power Generation | Maintains cleanliness in cooling water and lubricating oils. |
| Gas Production | Removes particulate matter from gases. |
| Food and Beverage | Ensures purity in food and beverage production processes. |
The versatility of sintered filters makes them indispensable in industries like chemical processing, petroleum refining, and food production.
How Does a Sintered Filter Work?
Filtration through a porous structure
Sintered filters rely on their unique porous structure to achieve efficient filtration. These filters consist of interconnected pores that create a complex, tortuous path for fluids or gases to pass through. This design enables two types of filtration:
- Surface filtration traps larger particles at the filter’s outer layer, preventing them from entering the system.
- Depth filtration captures smaller particles within the multiple layers of the filter, significantly increasing its dirt-holding capacity.
The porous structure also ensures consistent filtration performance by allowing a steady flow of fluids or gases while maintaining high filtration efficiency. This combination of surface and depth filtration makes sintered filters highly effective in removing impurities from liquids and gases.
Particle trapping and fluid or gas flow
Sintered filters operate on the principle of size exclusion. Particles larger than the pore size are trapped either on the surface or within the filter’s pores. The effectiveness of this process depends on factors such as particle size, flow rate, and the composition of the fluid or gas.
The sintering process, which compacts metal particles into a durable porous structure, enhances the filter’s ability to withstand harsh environments. This durability ensures that the filter remains effective even under extreme chemical or temperature conditions. As fluids or gases pass through the filter, the interconnected pores guide them along a winding path, capturing contaminants and ensuring clean output.
By combining advanced filtration techniques with robust materials, sintered filters provide reliable performance across various applications. Whether you’re dealing with industrial gases or liquids, these filters ensure optimal cleanliness and flow control.
Materials and Manufacturing Process

Common materials used in sintered filters
Sintered filters are crafted from a variety of materials, each chosen for its unique properties and suitability for specific applications. Below is a table highlighting the most commonly used materials and their characteristics:
| Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature tolerance, good mechanical properties | Chemical processing, food industry, extreme environments |
| Bronze | Good resistance to wear and corrosion, cost-effective | Seawater environments, applications requiring conductivity |
| Inconel® Alloys | Remarkable resistance to oxidation and corrosion in extreme environments | Chemical processing, pressure vessels |
| Nickel and Monel® | Excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity | Food processing, chemical industries |
These materials ensure that sintered filters perform reliably in challenging conditions, making them indispensable in industries like chemical processing and food production.
The sintering process explained
The sintering process transforms powdered materials into durable, porous structures. This process involves three key steps:
- Powder composing: You mix water, deflocculant, binder, and unfired ceramic powder to create a slurry. This step determines the filter’s strength and hardness.
- Powder compacting: The slurry undergoes mechanical densification through cold or hot mold pressing, forming a “green part” with precise tolerances.
- Sintering or firing: The green part is heated in a kiln, where particle fusion occurs through atom diffusion. This step enhances the filter’s density and strength.
This meticulous process ensures that sintered filters achieve the desired structural integrity and performance.
Characteristics of sintered materials
Sintered materials possess unique characteristics that set them apart from other filtration materials. The table below compares these features:
| Characteristic | Sintered Materials | Other Filtration Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Efficiency | High filtration efficiency | Varies by material |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited in some materials |
| Temperature Tolerance | High tolerance for temperature extremes | Varies significantly |
| Maintenance | Easy to maintain | Can be complex depending on material |
These attributes make sintered filters a reliable choice for demanding applications, ensuring efficiency and durability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sintered Filters

Key benefits of sintered filters
Sintered filters offer numerous advantages that make them a preferred choice across industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
- They perform exceptionally well under high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for demanding environments.
- Their ability to minimize waste at the source enhances efficiency in chemical processes.
- By improving product quality, they protect downstream equipment from damage caused by contaminants.
In addition to these, sintered filters stand out due to their:
- High porosity and permeability, which allow for greater fluid flow rates.
- Excellent particle retention capabilities, ensuring effective filtration.
- Durability in extreme conditions, including corrosive environments.
- Reduced maintenance costs, as they require less frequent replacements.
With proper care, these filters can last between 3 to 10 years or longer, significantly lowering operational costs. Their versatility also makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from aerospace to automotive industries.
Common limitations and challenges
Despite their many advantages, sintered filters come with a few challenges you should consider:
- The initial cost can be higher compared to disposable filter options.
- They may clog when exposed to heavy contaminant loads, requiring regular cleaning.
- Some types might have lower flow rates than non-sintered alternatives.
- Their limited pore size makes them unsuitable for ultra-fine particle filtration below 0.5 microns.
Understanding these limitations helps you make informed decisions when selecting a sintered filter for your specific needs. While these challenges exist, the benefits often outweigh them, especially in applications requiring durability and efficiency.
By addressing both the advantages and challenges, you gain a clearer picture of what sintered filters can offer. If you’re still wondering, “What is a Sintered Filter?” it’s a versatile solution that balances performance and longevity across various industries.
Applications of Sintered Filters

Industrial applications
Sintered filters play a vital role in various industrial processes by ensuring operational efficiency and product quality. Their ability to remove impurities and contaminants makes them indispensable in industries such as chemical processing, petroleum refining, and power generation. For example, in chemical processing, these filters purify and clarify substances, ensuring the removal of unwanted particles. In petroleum refining, they separate solids and contaminants from crude oil, enhancing the quality of the final product. Power generation facilities rely on sintered filters to maintain the cleanliness of cooling water and protect sensitive equipment from damage.
| Industry | Application Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Used to purify and clarify chemical substances, ensuring removal of impurities and contaminants. |
| Petroleum Refining | Crucial for separating and filtering solids and contaminants from crude oil and its derivatives. |
| Power Generation | Ensures cleanliness of cooling water and protects sensitive equipment from contamination. |
| Gas Production | Removes particulate matter and impurities to achieve high levels of gas purity. |
| Food & Beverage | Ensures cleanliness and purity of liquids and gases in food and beverage production processes. |
Use in water and air filtration
Sintered filters excel in water and air filtration systems due to their durability and efficiency. In water filtration, they remove sediments, contaminants, and impurities from drinking water and industrial wastewater. Their uniform pore structure ensures consistent performance, capturing particles of a specified size. Made from robust materials like stainless steel and titanium, these filters resist wear, pressure, and extreme temperatures. This makes them suitable for harsh environments. Additionally, their chemical and corrosion resistance enhances their longevity. You can clean and reuse these filters multiple times, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering operational costs.
Other industries and specialized uses
Sintered filters also find applications in niche industries requiring high precision and reliability. In gas production, they remove particulate matter and impurities, ensuring high gas purity. The food and beverage industry uses these filters to maintain hygiene and product quality during production. Their role in chemical processing and petroleum refining further highlights their versatility. Whether you need to purify chemicals, filter crude oil, or ensure cleanliness in food production, sintered filters provide a dependable solution. Their adaptability makes them a valuable asset across specialized industries.
If you’re still wondering, “What is a Sintered Filter?” it’s a versatile tool that enhances efficiency and reliability in diverse applications.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Effective cleaning methods
Maintaining the performance of your sintered filter requires regular cleaning to prevent material buildup and ensure optimal filtration. Several effective methods can help you achieve this:
- Backflushing: This method involves reversing the flow of fluid or gas through the filter. It dislodges contaminants trapped within the pores and flushes them out effectively.
- Ultrasonic cleaning: By immersing the filter in a cleaning solution and applying ultrasonic waves, you can remove stubborn particles that are difficult to dislodge through other methods.
- Chemical cleaning: Soaking the filter in a solvent dissolves contaminants. Always ensure the chosen chemicals are compatible with the filter material to avoid damage.
- Thermal cleaning: For filters exposed to high-temperature applications, heating the filter burns off contaminants. Follow this with backflushing or ultrasonic cleaning to remove residual ash.
💡 Tip: Regular inspection of your filter is essential. Look for signs of clogging or reduced flow rates, as these indicate the need for cleaning.
Tips to extend filter lifespan
To maximize the lifespan of your sintered filter, you should adopt proactive maintenance practices. Here are some practical tips:
- Conduct routine inspections to monitor wear and check for pressure drops.
- Follow a consistent cleaning schedule using methods like ultrasonic cleaning or backflushing to maintain performance.
- Operate the filter within its specified temperature and pressure limits to prevent material degradation.
- Monitor flow rates regularly. A noticeable drop in flow may signal the need for cleaning or replacement.
- Choose cleaning methods that align with the filter’s material and application to avoid unnecessary wear.
Pro Tip: Proper maintenance not only extends the filter’s lifespan but also ensures consistent filtration efficiency, reducing operational costs over time.
By implementing these cleaning methods and maintenance tips, you can keep your sintered filter in excellent condition, even in demanding environments.
Sintered filters stand out as indispensable tools across industries due to their efficiency and sustainability.
- They purify chemicals, refine petroleum, and ensure gas purity.
- Their recyclability and durability align with eco-friendly goals.
- High filtration efficiency and easy maintenance reduce waste and costs.
You can rely on them for consistent performance in demanding applications.
FAQ
What types of sintered filters does JHMIM offer?
JHMIM provides sintered stainless steel, bronze, titanium, and plastic filters. You can also request custom filters in various materials, shapes, and sizes.
How do you choose the right sintered filter?
Consider factors like filtration rating, pore size, chemical compatibility, working temperature, flow rate, and maintenance requirements. These ensure the filter meets your specific application needs.
How can you clean a sintered filter effectively?
Use methods like ultrasonic cleaning, chemical flushing, or pyrolytic burn-off. Always follow the recommended cleaning process to maintain the filter’s performance and longevity.
