Titanium 3D printing structural parts
3D printing is a type of rapid prototyping technology. It is a technology that is based on digital model files and uses adhesive materials such as powdered metal or plastic to construct objects by printing layer by layer. It is also called additive manufacturing.
Comparison of 3D printing and traditional manufacturing
| Traditional manufacturing |
VS. |
3D Printing |
| Mass production, quantity price | Small quantity production, uniform cost | |
| Normalization | Customization | |
| Subtractive manufacturing, product design is limited by mold | Additive manufacturing, can achieve any design | |
| Hand-made | Digitized manufacturing | |
| Labor-intensive | Brain intensive | |
| The distance between design and production line is far | Design is production, ready to respond to market demand |
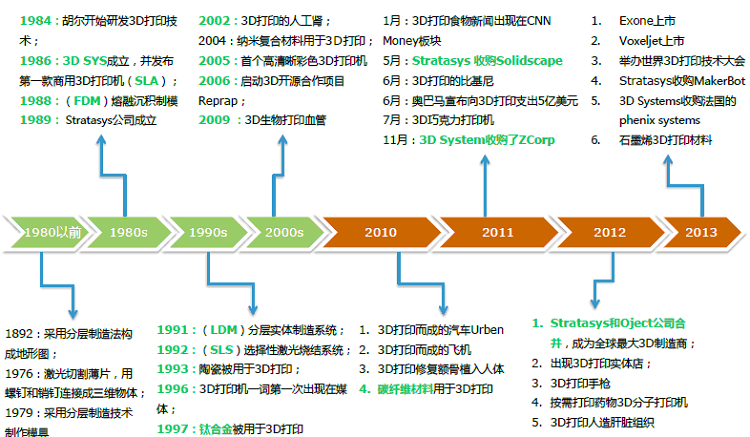
History of 3D printing
The main processes of 3D printing are:
- stereolithography
- Melt accumulation molding
- Layered physical manufacturing
- Electron beam melting
- Laser near-net molding
- Laser selection melting
| 3d printing process | Material |
| Stereolithography(SLA) | Acrylic resin, epoxy resin, vinyl ether resin |
| Fused Deposition Modeling(FDM) | Acrylic acid, butadiene-styrene, polycarbonate, polyester, polystyrene |
| laminated object manufacturing (LOM) | Aluminum, PVC, ABS, polycarbonate, polyester, titanium nitrite, ceramics, other metals |
| Electron beam melting(EBM) | Super heat resistant alloy, stainless steel, tool steel, aluminum, titanium, copper |
| laser engineered net shaping(LENS) | 316, 304, 17-4, stainless steel, Nickel-based superalloy, tungsten, copper, aluminum, M300 steel, H13 tool steel, titanium, low carbon steel, aluminum-nickel compounds |
| selective laser sintering(SLS) | Polystyrene, polycarbonate, polyamide, tungsten, copper, aluminum, low carbon steel |
At present, 3D printing has been widely used in industrial modeling, machinery manufacturing, military, architecture, film and television, home appliances, light industry, medicine, archaeology, culture and art, sculpture, jewelry and other fields, and with the development of technology, its application field continues to expand.
3d Printed titanium parts
-
Titanium alloy properties
Low density, high melting point, high strength, low thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance
-
Aerospace applications of titanium alloys
Mainly used in aircraft frames, engine compressor blades, spacecraft pressure vessels, fuel tanks, fasteners, structural parts, frames and rocket casings, etc.
-
3D printing of titanium alloy
It is very suitable for 3D printing because of its low density, high strength, high melting point, corrosion resistance, low thermal conductivity, and the fact that heat will not dissipate and cause local deformation when heated.
Advantages of 3d printed titanium
Achieve special-shaped complex structures, with the thinnest wall thickness up to 0.3mm~0.4mm;
Near net shape, accuracy up to 0.05mm;
At the same specific stiffness, the weight of 3D printing is reduced by more than 50% compared with traditional manufacturing;
Reduce costs and shorten processing cycles;
Able to minimize the cost of design changes;
Low-cost and rapid manufacturing of principle prototypes.
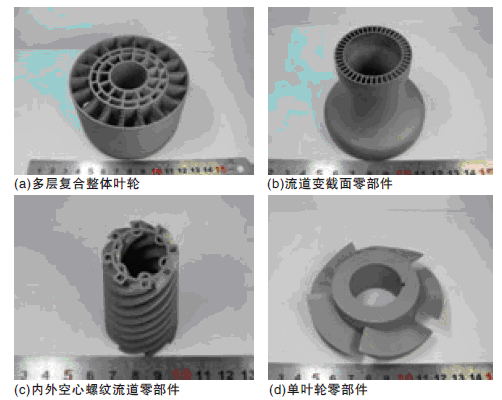

Titanium alloy parts produced by 3D printing technology

Titanium airplanes parts

Titanium products produced by 3D printing technology

Gears on the A380 landing gear manufactured by 3D printing technology
JH MIM, which started as MIM technology, has established a sound product ecology by investing in advantageous enterprises in related industries. Now it can provide customers with one-stop services such as Powder Metallurgy Process, Die Casting, CNC, and 3D printing. It is equipped with integrated assembly capabilities and the quality of quality suppliers mentioned above. Please click the link below for more detailed information.
