
Introduction
Helical gears are a crucial component in many industrial applications, known for their efficiency and smooth operation. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of helical gears is essential for selecting the right gear type for specific applications. This article explores the key benefits and drawbacks of helical gears, providing a comprehensive overview for engineers, procurement specialists, and industrial designers.
Advantages of Helical Gears
Helical gears offer numerous advantages that make them preferable in many mechanical and industrial applications.
Smoother and Quieter Operation
One of the most significant advantages of helical gears is their smoother and quieter operation compared to other gear types.
Reduced Noise Levels
Helical gears are designed with angled teeth, which engage gradually rather than suddenly. This gradual engagement reduces the noise levels during operation, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is critical. For instance, in automotive transmissions, the quieter operation of helical gears enhances the overall driving experience by minimizing the noise generated by the gearbox.
Enhanced Smoothness
The angled teeth of helical gears provide continuous contact between the gear teeth, resulting in smoother motion. This smooth operation reduces vibrations and contributes to the longevity of the machinery by minimizing wear and tear. In precision machinery, such as CNC machines, the smoothness of helical gears ensures accurate and reliable performance. Helical gears can achieve precision levels up to AGMA Grade 13, which corresponds to a tolerance range of ±0.001 inches (±0.025 mm), ensuring high accuracy in applications requiring fine adjustments.
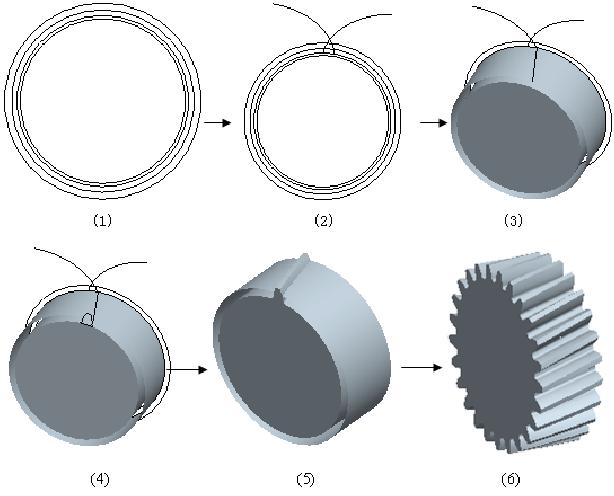
Higher Load Capacity
Helical gears are known for their superior load-carrying capacity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Load Distribution
The load in helical gears is distributed over multiple teeth simultaneously due to the helix angle. This distribution reduces the stress on individual teeth and increases the overall load capacity of the gear. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications requiring the transmission of high torque, such as industrial gearboxes and heavy machinery.
Applications in Heavy Machinery
In industries like mining, construction, and manufacturing, the ability to handle high loads is essential. Helical gears are commonly used in these sectors due to their robustness and reliability. For example, in conveyor systems used in mining operations, the high load capacity of helical gears ensures continuous and efficient operation under demanding conditions.
Greater Efficiency and Performance
Helical gears provide greater efficiency and performance in various applications due to their design and operation characteristics.
Increased Contact Ratio
Helical gears have a higher contact ratio compared to spur gears, meaning more teeth are in contact at any given time. This increased contact ratio enhances the efficiency of power transmission, reducing energy losses and improving overall performance. This is crucial in applications such as electric motors and turbines, where efficiency directly impacts operational costs and energy consumption.
Versatility in Applications
Helical gears are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, from low-speed, high-torque scenarios to high-speed, low-torque operations. Their ability to adapt to various operational requirements makes them a popular choice in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial automation.
Disadvantages of Helical Gears
Despite their advantages, helical gears also have certain drawbacks that need to be considered.
Axial Thrust and Load
One of the main disadvantages of helical gears is the generation of axial thrust and load.
Axial Force Generation
The angled teeth of helical gears create axial forces as they engage. These forces act parallel to the gear shaft, requiring additional components to counteract them. In applications where axial load is a concern, this can complicate the design and increase the cost of the gear system.
Bearing Requirements
To handle the axial thrust generated by helical gears, specialized bearings are often needed. These bearings must be designed to withstand both radial and axial loads, which can increase the overall cost and complexity of the system. In high-speed applications, the need for advanced bearing solutions becomes even more critical.
Complex Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of helical gears is more complex compared to spur gears.
Precision Requirements
Helical gears require precise manufacturing techniques to ensure the correct tooth angle and alignment. Any deviation can result in poor performance and increased wear. This precision adds to the manufacturing complexity and requires advanced machinery and skilled labor. The production of helical gears often involves CNC machining and grinding processes that can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.0005 inches (±0.0127 mm).
Higher Initial Costs
Due to the complexity of their design and manufacturing process, helical gears typically have higher initial costs than other gear types. However, this initial investment can be offset by the benefits of improved performance, reduced maintenance, and longer lifespan.
Lubrication and Maintenance Needs
Helical gears require adequate lubrication and maintenance to operate effectively.
Increased Friction
The sliding contact between the teeth in helical gears generates more friction compared to spur gears. This friction necessitates effective lubrication to prevent excessive wear and overheating. Inadequate lubrication can lead to premature failure and increased maintenance costs.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of helical gears. This includes monitoring the lubrication levels, checking for wear, and ensuring proper alignment. While this maintenance can increase operational costs, it is crucial for preventing unexpected downtime and extending the life of the gear system.
Applications of Helical Gears
Helical gears are widely used in various industries due to their unique advantages.
Automotive Industry
Helical gears are extensively used in the automotive industry.
Gearboxes and Transmissions
In automotive gearboxes, helical gears provide smooth and quiet operation, which enhances the driving experience. Their ability to handle high loads and transmit power efficiently makes them ideal for modern transmissions.
Industrial Machinery
Helical gears are a staple in industrial machinery.
Heavy Equipment and Machinery
In heavy equipment and machinery, such as excavators and cranes, helical gears ensure reliable and efficient operation under high load conditions. Their durability and load-carrying capacity are crucial for these demanding applications.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry also relies on helical gears.
Aircraft Components
Helical gears are used in various aircraft components, where reliability and performance are critical. Their ability to operate smoothly and quietly under high loads makes them suitable for applications such as aircraft engines and control systems.
Conclusion
Helical gears offer numerous advantages, including smoother and quieter operation, higher load capacity, and greater efficiency. However, they also have disadvantages, such as axial thrust, complex manufacturing processes, and the need for regular maintenance. Understanding these pros and cons is essential for selecting the right gear type for specific applications. As a leading provider of custom powder metallurgy gear metal parts, we leverage the benefits of helical gears to deliver high-performance solutions to our clients. For more information on how helical gears can enhance your operations,
More resources
